This is a preprint.
Genome-wide dynamic nascent transcript profiles reveal that most paused RNA polymerases terminate
- PMID: 40196675
- PMCID: PMC11974822
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.27.645809
Genome-wide dynamic nascent transcript profiles reveal that most paused RNA polymerases terminate
Abstract
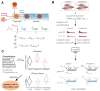
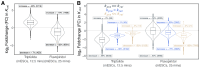
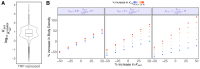
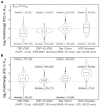
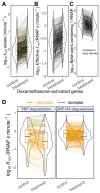
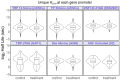
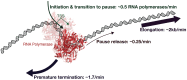
We present a simple model for analyzing and interpreting data from kinetic experiments that measure engaged RNA polymerase occupancy. The framework represents the densities of nascent transcripts within the pause region and the gene body as steady-state values determined by four key transcriptional processes: initiation, pause release, premature termination, and elongation. We validate the model's predictions using data from experiments that rapidly inhibit initiation and pause release. The model successfully classified factors based on the steps in early transcription that they regulate, confirming TBP and ZNF143 as initiation factors and HSF and GR as pause release factors. We found that most paused polymerases terminate and paused polymerases are short-lived with half lives less than a minute. We make this model available as software to serve as a quantitative tool for determining the kinetic mechanisms of transcriptional regulation.
Keywords: Compartment Model; Initiation; PRO-seq; Premature termination; Promoter-proximal pausing; Transcription regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
STL-seq reveals pause-release and termination kinetics for promoter-proximal paused RNA polymerase II transcripts.Mol Cell. 2021 Nov 4;81(21):4398-4412.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.08.019. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34520723 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of a nascent RNA structure with RNA polymerase is required for hairpin-dependent transcriptional pausing but not for transcript release.Genes Dev. 1998 Oct 1;12(19):3110-22. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.19.3110. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9765211 Free PMC article.
-
Model-based characterization of the equilibrium dynamics of transcription initiation and promoter-proximal pausing in human cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Nov 27;51(21):e106. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad843. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37889042 Free PMC article.
-
Pause & go: from the discovery of RNA polymerase pausing to its functional implications.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017 Jun;46:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28363125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promoter-proximal regulation of gene transcription: Key factors involved and emerging role of general transcription factors in assisting productive elongation.Gene. 2023 Aug 20;878:147571. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147571. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Gene. 2023. PMID: 37331491 Review.
References
-
- Saunders A, Core LJ, Lis JT. Breaking barriers to transcription elongation. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2006;7(8):557–567. - PubMed
-
- Rougvie AE, Lis JT. The RNA polymerase II molecule at the 5 end of the uninduced hsp70 gene of D. melanogaster is transcriptionally engaged. Cell. 1988;54(6):795–804. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
