Estrogen-induced FXR1 promotes endocrine resistance and bone metastasis in breast cancer via BCL2 and GPX4
- PMID: 40196843
- PMCID: PMC11973456
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1563353
Estrogen-induced FXR1 promotes endocrine resistance and bone metastasis in breast cancer via BCL2 and GPX4
Abstract
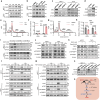
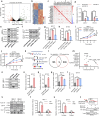
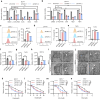
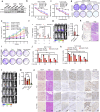
Estrogen signaling dysregulation plays a critical role in the development of anti-estrogen resistance and bone metastasis of ER+ mammary carcinoma. Using quantitative proteomic screening, we identified FXR1 as an estrogen-regulated RNA-binding protein associated with anti-estrogen resistance. Mechanistically, estrogen and IGF1 facilitate FXR1 protein translation via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/EIF4E pathway. FXR1 enhances cellular resistance to apoptosis and ferroptosis by facilitating the maturation of BCL2 pre-mRNA and stabilizing GPX4 mRNA, respectively. Anti-estrogen resistant cells exhibit elevated FXR1 expression, and FXR1 depletion restores their sensitivity to tamoxifen. Moreover, combining FXR1 depletion with a ferroptosis inducer induces synergistic lethal in anti-estrogen resistant cells. Finally, we provide proof-of-concept evidence supporting FXR1 antagonism as a potential treatment for bone metastases in ER+ breast cancer. Our findings highlight FXR1 as a promising therapeutic target to improve existing therapeutic regimes for ER+ breast cancer patients.
Keywords: FXR1; anti-estrogen resistance; apoptosis; estrogen; ferroptosis.
Copyright © 2025 Shang, Cao, Ma, Huang, Wu, Xu, Wang, Wang, Wu, Pandey, Wu, Zhang, Lobie, Han and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bartha Á., Győrffy B. (2021). TNMplot.com: a web Tool for the comparison of gene expression in normal, tumor and Metastatic tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (5), 2622. 10.3390/ijms22052622 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

