Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 40196891
- PMCID: PMC12167664
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaf167
Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
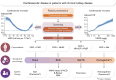
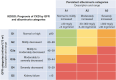
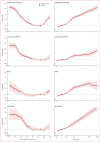
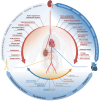
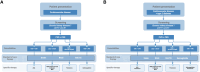
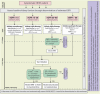
Individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD) exhibit an increased risk for the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD) with its manifestations coronary artery disease, stroke, heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death. The presence of both, CVD and CKD has a major impact on the prognosis of patients. This association likely reflects the involvement of several pathophysiological mechanisms, including shared risk factors (e.g. diabetes and hypertension), as well as other factors such as inflammation, anaemia, volume overload, and the presence of uraemic toxins. Identifying and characterizing CKD is crucial for appropriate CVD risk prediction. Mitigating CVD risk in patients with CKD mandates a multidisciplinary approach involving cardiologists, nephrologists, and other health care professionals. The present State-of-the-Art Review addresses the current understanding on the pathophysiological link between CVD and CKD, clinical implications and challenges in the treatment of these patients.
Keywords: CV risk; Cardiovascular disease; Chronic kidney disease; GLP-1 receptor agonists; Non-steroidal MRAs; SGLT2 inhibitors.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

