S-propargyl-cysteine attenuates temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by regulating macrophage polarization via Inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling
- PMID: 40197110
- PMCID: PMC11974036
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-025-01186-6
S-propargyl-cysteine attenuates temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by regulating macrophage polarization via Inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling
Erratum in
-
Correction: S-propargyl-cysteine attenuates temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by regulating macrophage polarization via Inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling.Mol Med. 2025 Apr 28;31(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01214-5. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40295904 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis (TMJ-OA) is a disease characterized by cartilage degradation and synovial inflammation, with limited effective treatment currently. Synovial macrophage polarization is pivotal in TMJ-OA progression, making it a promising therapeutic aspect. This study investigated the effects of S-propargyl-cysteine (SPRC), an endogenous H2S donor, on macrophage polarization and its therapeutic potential in alleviating TMJ-OA.
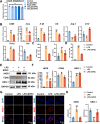
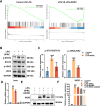
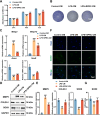
Methods: A MIA-induced TMJ-OA rat model and LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages were employed to evaluate the effects of SPRC in vivo and in vitro. TMJ bone and cartilage were analyzed via micro-CT and histological methods, while macrophage polarization markers expression were assessed via RT-qPCR, western blot, and immunofluorescence. RNA sequencing was performed on macrophages, and the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway was validated using the JAK2-specific inhibitor AG490. The direct effects of SPRC on rat primary condylar chondrocytes were examined by evaluating ECM synthesis and degradation. Co-culture experiments further assessed macrophage-chondrocyte interactions.
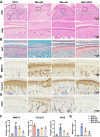
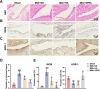
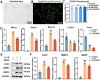
Results: SPRC significantly alleviated cartilage and bone damage in the TMJ-OA rat model, as demonstrated by improved bone volume and cartilage structure. SPRC reduced pro-inflammatory M1 macrophage infiltration and enhanced anti-inflammatory M2 macrophage polarization. SPRC effectively inhibited the JAK2/STAT3, leading to reduction of inflammatory markers, including TNF-α, IL-6, and iNOS. Co-culture experiments revealed that SPRC-treated macrophage-conditioned medium improved chondrocyte metabolic activity and restored ECM integrity.
Conclusions: SPRC-modulated macrophage polarization alleviates TMJ-OA via JAK/STAT downregulation, thereby reducing synovial inflammation and cartilage degradation. These findings position SPRC as a promising therapeutic candidate for TMJ-OA and provide insights into novel strategies targeting macrophage polarization and synovium-cartilage crosstalk.
Keywords: Hydrogen sulfide; JAK/STAT; Macrophage; S-propargyl-cysteine; Synovial; Temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Guangdong HUA WEI Testing Co., Ltd. Ethics Committee (No. 202310002). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Cardoneanu A, Macovei LA, Burlui AM, Mihai IR, Bratoiu I, Rezus II, Richter P, Tamba BI, Rezus E. Temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: pathogenic mechanisms involving the cartilage and subchondral bone, and potential therapeutic strategies for joint regeneration. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 24(1). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

