Unveiling the crossroads of STING signaling pathway and metabolic reprogramming: the multifaceted role of the STING in the TME and new prospects in cancer therapies
- PMID: 40197235
- PMCID: PMC11977922
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-025-02169-0
Unveiling the crossroads of STING signaling pathway and metabolic reprogramming: the multifaceted role of the STING in the TME and new prospects in cancer therapies
Abstract
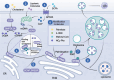
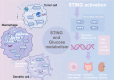
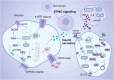
The cGAS-STING signaling pathway serves as a critical link between DNA sensing and innate immunity, and has tremendous potential to improve anti-tumor immunity by generating type I interferons. However, STING agonists have shown decreasing biotherapeutic efficacy in clinical trials. Tumor metabolism, characterized by aberrant nutrient utilization and energy production, is a fundamental hallmark of tumorigenesis. And modulating metabolic pathways in tumor cells has been discovered as a therapeutic strategy for tumors. As research concerning STING progressed, emerging evidence highlights its role in metabolic reprogramming, independent its immune function, indicating metabolic targets as a strategy for STING activation in cancers. In this review, we delve into the interplay between STING and multiple metabolic pathways. We also synthesize current knowledge on the antitumor functions of STING, and the metabolic targets within the tumor microenvironment (TME) that could be exploited for STING activation. This review highlights the necessity for future research to dissect the complex metabolic interactions with STING in various cancer types, emphasizing the potential for personalized therapeutic strategies based on metabolic profiling.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhancing immunotherapy outcomes by targeted remodeling of the tumor microenvironment via combined cGAS-STING pathway strategies.Front Immunol. 2024 May 16;15:1399926. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1399926. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38817608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing radiotherapy-induced anti-tumor immunity via nanoparticle-mediated STING agonist synergy.Mol Cancer. 2025 Jun 11;24(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02366-y. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40500702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pleiotropic roles of cGAS-STING signaling in the tumor microenvironment.J Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Aug 5;14(4):mjac019. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjac019. J Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35325182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cytosolic DNA-Sensing cGAS-STING Pathway in Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2020 Jan;10(1):26-39. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0761. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 31852718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting STING for cancer immunotherapy: From mechanisms to translation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Dec;113(Pt A):109304. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109304. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36252492 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of the gut microbiota in shaping the tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy of breast cancer.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 27;16:1591745. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1591745. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40497049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ablasser, A. & Chen, Z. J. cGAS in action: Expanding roles in immunity and inflammation. Science 363, eaat8657 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Xu P. Cellular functions of cGAS-STING signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2023;33:630–48. - PubMed
-
- Samson N, Ablasser A. The cGAS-STING pathway and cancer. Nat Cancer. 2022;3:1452–63. - PubMed
-
- Zhao K, et al. Targeting STING in cancer: Challenges and emerging opportunities. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023;1878: 188983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

