Computational mechanisms underlying the impact of Pavlovian bias on instrumental learning in problematic social media users
- PMID: 40198130
- PMCID: PMC12231439
- DOI: 10.1556/2006.2025.00026
Computational mechanisms underlying the impact of Pavlovian bias on instrumental learning in problematic social media users
Abstract
Background and aims: Problematic social media use (PSMU), a potential behavioral addiction, has become a worldwide mental health concern. An imbalanced interaction between Pavlovian and instrumental learning systems has been proposed to be central to addiction. However, it remains unclear whether individuals with PSMU also over-rely on the Pavlovian system when flexible instrumental learning is required.
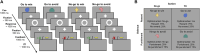
Methods: To address this question, we used an orthogonalized go/no-go task that distinguished two axes of behavioral control during associative learning: valence (reward or punishment) and action (approach or avoidance). We compared the learning performance of 33 individuals with PSMU and 32 regular social media users in this task. Moreover, latent cognitive factors involved in this task, such as learning rate and reward sensitivity, were estimated using a computational modeling approach.
Results: The PSMU group showed worse learning performance when Pavlovian and instrumental systems were incongruent in the reward, but not the punishment, domain. Computational modeling results showed a higher learning rate and lower reward sensitivity in the PSMU group than in the control group.
Conclusions: This study elucidated the computational mechanisms underlying suboptimal instrumental learning in individuals with PSMU. These findings not only highlight the potential of computational modeling to advance our understanding of PSMU, but also shed new light on the development of effective interventions for this disorder.
Keywords: Pavlovian bias; computational modeling; instrumental learning; problematic social media use; reward sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Brand, M., Rumpf, H. J., Demetrovics, Z., Müller, A., Stark, R., King, D. L., … Potenza, M. N. (2020). Which conditions should be considered as disorders in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11) designation of “other specified disorders due to addictive behaviors”. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 11(2), 150–159. 10.1556/2006.2020.00035. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brand, M., Wegmann, E., Stark, R., Müller, A., Wölfling, K., Robbins, T. W., & Potenza, M. N. (2019). The Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-PACE) model for addictive behaviors: Update, generalization to addictive behaviors beyond internet-use disorders, and specification of the process character of addictive behaviors. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 104, 1–10. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.06.032. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

