Identification of CD84 as a potent survival factor in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 40198133
- PMCID: PMC12126229
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI176818
Identification of CD84 as a potent survival factor in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
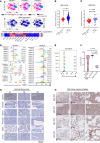
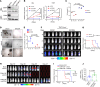
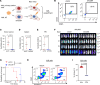
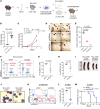
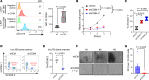
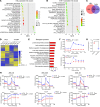
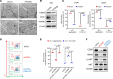
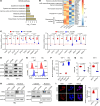
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive and often deadly malignancy associated with proliferative immature myeloid blasts. Here, we identified CD84 as a critical survival regulator in AML. High levels of CD84 expression provided a survival advantage to leukemia cells, whereas CD84 downregulation disrupted their proliferation, clonogenicity, and engraftment capabilities in both human cell lines and patient-derived xenograft cells. Critically, loss of CD84 also markedly blocked leukemia engraftment and clonogenicity in MLL-AF9 and inv(16) AML mouse models, highlighting its pivotal role as a survival factor across species. Mechanistically, CD84 regulated leukemia cells' energy metabolism and mitochondrial dynamics. Depletion of CD84 altered mitochondrial ultrastructure and function of leukemia cells, and it caused downmodulation of both oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid oxidation pathways. CD84 knockdown induced a block of Akt phosphorylation and downmodulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), impairing AML antioxidant defense. Conversely, CD84 overexpression stabilized NRF2 and promoted its transcriptional activation, thereby supporting redox homeostasis and mitochondrial function in AML. Collectively, our findings indicate that AML cells depend on CD84 to support antioxidant prosurvival pathways, highlighting a therapeutic vulnerability of leukemia cells.
Keywords: Antigen; Bone marrow; Cancer immunotherapy; Cell biology; Hematology; Oncology.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

