Cerebrospinal-fluid Orexin-A levels in different neurocognitive disorders: a comparison study
- PMID: 40198471
- PMCID: PMC12267319
- DOI: 10.1007/s10072-025-08148-0
Cerebrospinal-fluid Orexin-A levels in different neurocognitive disorders: a comparison study
Abstract
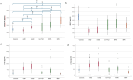
In the present study, we investigated the differences in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) orexin-A levels among patients with different neurocognitive disorders, such as mild or moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease (AD; mAD, msAD, respectively), behavioral variants of frontotemporal dementia (bv-FTD), non-fluent primary aphasia (NFPA), and idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH). A total of 214 participants were evaluated (mAD, 45; msAD, 31; bv-FTD, 12; NFPA, 22; iNPH, 13; non-demented elderly controls, 91). The highest CSF orexin-A levels were found in iNPH patients (263.31 ± 56.89 pg/mL). Patients affected by NFPA (210.86 ± 61.99 pg/mL), iNPH, and msAD (173.04 ± 19.76 pg/mL) showed higher CSF orexin-A concentrations than controls (145.18 ± 27.01pg/mL) (p < 0.001). Bv-FTD (190.12 ± 100.84 pg/mL) and mAD (130.76 ± 21.70 pg/mL) patients showed no significant differences in CSF orexin-A levels compared with controls. mAD patients showed also lower CSF orexin-A concentrations than all other patient groups.In conclusion, orexin-A presents different CSF levels among neurocognitive disorders. The mechanisms underlying this difference vary and may include sleep-wake cycle impairment, behavioral disturbances, and CSF dynamics. The development of drugs that antagonize the orexin system could open a new frontier of research linking orexin neurotransmission to neurocognitive disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Cognitive impairment; Dementia; FTD; Orexin-A; iNPH; tau; β-amyloid.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethicals approval: Claudio Liguori received research support from Idorsia and attended advisory boards or consultation organized by EISAI, MSD and Idorsia. Informed consent: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants enrolled in the study for the management of clinical and biological data. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Saper CB, Scammell TE, Lu J (2005) Hypothalamic regulation of sleep and circadian rhythms. Nature 437(7063):1257–1263 - PubMed
-
- Nepovimova E, Janockova J, Misik J, Kubik S, Stuchlik A, Vales K et al (2019) Orexin-A supplementation in narcolepsy treatment: A review. Med Res Rev 39(3):961–975 - PubMed
-
- Toor B, Ray LB, Pozzobon A, Fogel SM, Sleep (2021) Orexin-A and cognition. Front Neurol Neurosci 45:38–51 - PubMed
-
- Sakurai T, Saito YC, Yanagisawa M (2021) Interaction between orexin neurons and monoaminergic systems. Front Neurol Neurosci 45:11–21 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources