A study on innovation resistance of artificial intelligence voice assistants based on privacy infringement and risk perception
- PMID: 40198618
- PMCID: PMC11978003
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320431
A study on innovation resistance of artificial intelligence voice assistants based on privacy infringement and risk perception
Abstract
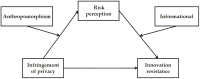
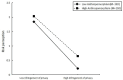
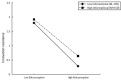
As a vital tool for human-computer interaction, artificial intelligence (AI) voice assistants have become an integral part of individuals' everyday routines. However, there are still a series of problems caused by privacy violations in current use. This research aims to explore users' risk perceptions and innovation resistance arising from privacy concerns when utilizing AI voice assistants. Descriptive statistics and correlation analysis were conducted using SPSS21.0 software to examine each variable. The mediating and moderating effects were analyzed through specific models provided by PROCESS. The findings of this research indicate that perceptions of risk serve as a mediator in the relationship between privacy violations and resistance to innovation. This elucidates the indirect pathway through which privacy concerns impact opposition to new technologies. Furthermore, the study reveals that anthropomorphism and informativeness can mitigate the perceived risks associated with AI voice assistants, consequently reducing resistance to innovation. By focusing on user psychology, this study offers valuable insights for the development and enhancement of AI voice assistants, underscoring the importance of addressing user concerns regarding privacy and risk.
Copyright: © 2025 Liu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Ramana TV, Ghantasala GSP, Sathiyaraj R, Khan M. Artificial intelligence and machine learning for smart community: concepts and applications. 2024.
-
- Cho Y. IoT and media industry: landscape of home market competition. Stu Bro Cul. 2016;8(1):87–120. doi: 10.22854/sbc.2016.28.1.87 - DOI
-
- Lee E, Cho M, Ahn H, Sung Y. Facebook ambivalence by user characteristics. J HCI Soc Kor. 2018;13(3):43–53. doi: 10.17210/jhsk.2018.08.13.3.43 - DOI
-
- Yin L, Li Y. Personal sharing and privacy protection in social media from the perspective of internet governance. J Commun. 2016;23(1):69–77.
-
- Chua HN, Ooi JS, Herbland A. The effects of different personal data categories on information privacy concern and disclosure. Comput Secur. 2021;110:102453. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2021.102453 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials