Membrane Charge Drives the Aggregation of TDP-43 Pathological Fragments
- PMID: 40198794
- PMCID: PMC12022992
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c00594
Membrane Charge Drives the Aggregation of TDP-43 Pathological Fragments
Abstract
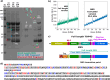
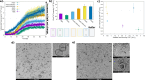
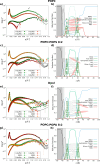
TDP-43 protein is an RNA-binding protein linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, frontotemporal dementia, and Alzheimer disease. While normally a protein that shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm, TDP-43 has recently been found also in extracellular vesicles. These are an important medium for cell-cell communication that allows the transfer of lipids, proteins, and genetic material among cells. An increasing concern in neurodegenerative diseases, however, is the possibility that extracellular vesicles can also provide an effective way to spread misfolded proteins that could "infect" other cells according to a "prion-like" mechanism. To characterize the interaction of TDP-43 with lipid membranes, we carried out a systematic biophysical study using a TDP-43 fragment lacking the first 84 N-terminal residues, called M85, and synthetic model phospholipid membranes. We utilized standard techniques, such as fluorescence and microscopy, complemented by neutron reflectivity measurements. Our results show that lipid charge affects the modality by which M85 interacts with membranes: a higher negative charge induces the protein to bind to the bilayer surface, promoting protein aggregation and decreasing lipid bilayer damage that this interaction causes. Thus, we speculate that the M85-lipid membrane interaction could play an important and previously undefined role in TDP-43-related neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Neumann M.; Sampathu D. M.; Kwong L. K.; Truax A. C.; Micsenyi M. C.; Chou T. T.; Bruce J.; Schuck T.; Grossman M.; Clark C. M.; McCluskey L. F.; Miller B. L.; Masliah E.; Mackenzie I. R.; Feldman H.; Feiden W.; Kretzschmar H. A.; Trojanowski J. Q.; Lee V. M. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2006, 314 (5796), 130–133. 10.1126/science.1134108. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arai T.; Hasegawa M.; Akiyama H.; Ikeda K.; Nonaka T.; Mori H.; Mann D.; Tsuchiya K.; Yoshida M.; Hashizume Y.; Oda T. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351 (3), 602–11. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.093. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Igaz L. M.; Kwong L. K.; Lee E. B.; Chen-Plotkin A.; Swanson E.; Unger T.; Malunda J.; Xu Y.; Winton M. J.; Trojanowski J. Q.; Lee V. M. Y. Dysregulation of the ALS-Associated Gene TDP-43 Leads to Neuronal Death and Degeneration in Mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121 (2), 726–738. 10.1172/JCI44867. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

