Online Information About Side Effects and Safety Concerns of Semaglutide: Mixed Methods Study of YouTube Videos
- PMID: 40198905
- PMCID: PMC12015341
- DOI: 10.2196/59767
Online Information About Side Effects and Safety Concerns of Semaglutide: Mixed Methods Study of YouTube Videos
Abstract
Background: Social media has been extensively used by the public to seek information and share views on health issues. Recently, the proper and off-label use of semaglutide drugs for weight loss has attracted huge media attention and led to temporary supply shortages.
Objective: The aim of this study was to perform a content analysis on English YouTube (Google) videos related to semaglutide.
Methods: YouTube was searched with the words semaglutide, Ozempic, Wegovy, and Rybelsus. The first 30 full-length videos (videos without a time limit) and 30 shorts (videos that are no longer than 1 minute) resulting from each search word were recorded. After discounting duplicates resulting from multiple searches, a total of 96 full-length videos and 93 shorts were analyzed. Video content was evaluated by 3 tools, that is, a custom checklist, a Global Quality Score (GQS), and Modified DISCERN. Readability and sentiment of the transcripts were also assessed.
Results: There was no significant difference in the mean number of views between full-length videos and shorts (mean 288,563.1, SD 513,598.3 vs mean 188,465.2, SD 780,376.2, P=.30). The former had better content quality in terms of GQS, Modified DISCERN, and the number of mentioned points from the custom checklist (all P<.001). The transcript readability of both types of videos was at a fairly easy level and mainly had a neutral tone. Full-length videos from health sources had a higher content quality in terms of GQS and Modified DISCERN (both P<.001) than their counterparts.
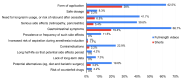
Conclusions: The analyzed videos lacked coverage of several important aspects, including the lack of long-term data, the persistence of side effects due to the long half-life of semaglutide, and the risk of counterfeit drugs. It is crucial for the public to be aware that videos cannot replace consultations with physicians.
Keywords: Ozempic; Rybelsus; Wegovy; YouTube; assessment; consultation; drugs; health issues; knowledge exchange; long-term data; online; online information; safety; semaglutide; side effects; social media; videos; weight loss.
©Andy Wai Kan Yeung, Fabian Peter Hammerle, Sybille Behrens, Maima Matin, Michel-Edwar Mickael, Olena Litvinova, Emil D Parvanov, Maria Kletecka-Pulker, Atanas G Atanasov. Originally published in JMIR Infodemiology (https://infodemiology.jmir.org), 08.04.2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Chew C, Eysenbach G. Pandemics in the age of Twitter: content analysis of tweets during the 2009 H1N1 outbreak. PLoS One. 2010;5(11):e14118. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014118. https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0014118 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li HOY, Bailey A, Huynh D, Chan J. YouTube as a source of information on COVID-19: a pandemic of misinformation? BMJ Glob Health. 2020;5(5):e002604. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-002604. https://gh.bmj.com/lookup/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=32409327 bmjgh-2020-002604 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Inoue M, Shimoura K, Nagai-Tanima M, Aoyama T. The relationship between information sources, health literacy, and COVID-19 knowledge in the COVID-19 infodemic: cross-sectional online study in Japan. J Med Internet Res. 2022;24(7):e38332. doi: 10.2196/38332. https://www.jmir.org/2022/7/e38332/ v24i7e38332 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moon H, Lee GH. Evaluation of Korean-language COVID-19-related medical information on YouTube: cross-sectional infodemiology study. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(8):e20775. doi: 10.2196/20775. https://www.jmir.org/2020/8/e20775/ v22i8e20775 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lordan R, Devkota HP. Turbulence at Twitter with leadership change: implications for health research and science communication. Explor Digit Health Technol. 2023 Nov 1;1:4–10. doi: 10.37349/edht.2023.00002. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

