Real-world outcomes of brentuximab vedotin as consolidation therapy after autologous stem cell transplantation in relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40200006
- PMCID: PMC12151861
- DOI: 10.1038/s41409-025-02557-7
Real-world outcomes of brentuximab vedotin as consolidation therapy after autologous stem cell transplantation in relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Brentuximab vedotin (BV) as post-autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) consolidation was shown to reduce the relapse risk among high-risk patients with relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma (RRHL) in the clinical trial setting. This systematic review and meta-analysis characterizes real-world evidence (RWE) on the effectiveness and safety of BV as post-ASCT consolidation in 1504 adult and pediatric patients with RRHL from 23 studies across 17 countries. A random-effects model yielded pooled progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival rates (OS); PFS: 2-year, 74.2%; 5-year, 65.8%; OS: 2-year, 95.8%; 5-year, 91.9%. The most common any-grade adverse events were neuropathy (34.2%) and neutropenia (20.2%). Despite heterogeneity in populations and outcomes, this analysis utilizing real-world data corroborates the efficacy and safety of BV as post-ASCT consolidation in RRHL reported in the experimental arm of the Phase III AETHERA trial. The favorable PFS results in cases exposed to BV prior to ASCT indicate the value of BV in controlling Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) in the salvage setting. Continued research is essential to refine BV treatment strategies amid the evolving treatment landscape.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Anna Sureda reports honoraria from Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Janssen, Amgen, Novartis, Kite/Gilead, Sanofi, Roche, and Alexion; consultancy for Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Novartis, Janssen, Gilead, and Sanofi; speakers bureau for Takeda Pharmaceuticals; research support from Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene; and Presidency of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Astrid Pavlovsky reports grants or contracts from Takeda Pharmaceuticals; consulting fees from Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Merck Sharp & Dohme; and support from Roche and Takeda Pharmaceuticals to attend meetings. Dalah Haidar, Fjoralba Kristo, Vanessa Stache, and Athanasios Zomas are employees of Takeda Pharmaceuticals and hold shares in the company.
Figures
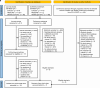





References
-
- Hoppe RT, Advani RH, Ai WZ, Ambinder RF, Armand P, Bello CM, et al. Hodgkin lymphoma, Version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020;18:755–81. - PubMed
-
- Engert A, Diehl V, Franklin J, Lohri A, Dorken B, Ludwig WD, et al. Escalated-dose BEACOPP in the treatment of patients with advanced-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma: 10 years of follow-up of the GHSG HD9 study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4548–54. - PubMed
-
- Gordon LI, Hong F, Fisher RI, Bartlett NL, Connors JM, Gascoyne RD, et al. Randomized phase III trial of ABVD versus Stanford V with or without radiation therapy in locally extensive and advanced-stage Hodgkin lymphoma: an intergroup study coordinated by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (E2496). J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:684–91. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carde P, Karrasch M, Fortpied C, Brice P, Khaled H, Casasnovas O, et al. Eight cycles of ABVD versus four cycles of BEACOPPescalated plus four cycles of BEACOPPbaseline in Stage III to IV, International Prognostic Score >/= 3, high-risk Hodgkin lymphoma: first results of the Phase III EORTC 20012 Intergroup Trial. J Clin Oncol 2016;34:2028–36. - PubMed
-
- Borchmann P, Goergen H, Kobe C, Lohri A, Greil R, Eichenauer DA, et al. PET-guided treatment in patients with advanced-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HD18): final results of an open-label, international, randomised phase 3 trial by the German Hodgkin Study Group. Lancet. 2017;390:2790–802. - PubMed

