Deciphering the impact of sepsis phenotypes on improving clinical outcome predictions: a multicenter retrospective analysis based on critical care in China
- PMID: 40200027
- PMCID: PMC11978960
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-93961-y
Deciphering the impact of sepsis phenotypes on improving clinical outcome predictions: a multicenter retrospective analysis based on critical care in China
Abstract
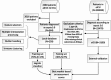
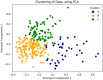
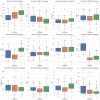
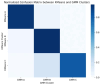
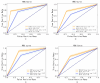
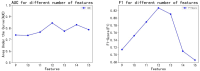
Sepsis is a clinically heterogeneous disease with high mortality. It is crucial to develop relevant therapeutic strategies for different sepsis phenotypes, but the impact of phenotypes on patients' clinical outcomes is unclear. This study aimed to identify potential sepsis phenotypes using readily available clinical parameters and assess their predictive value for 28-day clinical outcomes by logistic regression analysis. In this retrospective analysis, researchers extracted clinical data from adult patients admitted to the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University between April and August 2022 and from the 2014-2015 eICU Collaborative Study database. K-Means clustering was utilized to identify and refine sepsis phenotypes, and their predictive performance was subsequently evaluated. Logistic regression models were trained independently for each phenotype and five-fold cross-validation was used to predict clinical outcomes. Predictive accuracy was then compared to traditional non-clustered prediction methods using model assessment scores. The study cohort consisted of 250 patients from the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, allocated in a 7:3 ratio for training and testing, respectively, and an external validation cohort of 3100 patients from the eICU Cooperative Research Database. The results of the phenotype-based prediction model demonstrated an improvement in F1 score from 0.74 to 0.82 and AUC from 0.74(95%CI 0.71-0.80) to 0.84(95%CI 0.82-0.87), and these results also highlight the superiority of clinical outcome prediction with the help of sepsis phenotypes over traditional prediction methods. Phenotype-based prediction of 28-day clinical outcomes in sepsis demonstrated significant advantages over traditional models, highlighting the impact of phenotype-driven modeling on clinical outcomes in sepsis.
Keywords: Clustering algorithms; Intensive care; Machine learning; Phenotypes; Sepsis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Informed consent: The study protocol was approved by the research ethics board of our institution, and all patients provided informed consent before their medical records was reviewed. The performance of this study conformed with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figures
References
-
- Verdonk, F., Blet, A. & Mebazaa, A. The new sepsis definition. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol.30 (2), 200–204. 10.1097/aco.0000000000000446 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Peach, B. C. Implications of the new sepsis definition on research and practice. J. Crit. Care38, 259–262. 10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.11.032 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

