Subclonal response heterogeneity to define cancer organoid therapeutic sensitivity
- PMID: 40200028
- PMCID: PMC11978853
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-96204-2
Subclonal response heterogeneity to define cancer organoid therapeutic sensitivity
Abstract
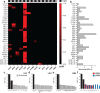
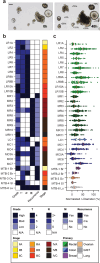
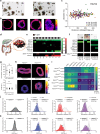
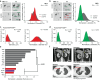
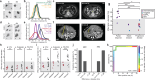
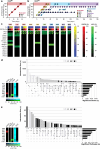
Tumor heterogeneity is predicted to confer inferior clinical outcomes with precision-based strategies, however, modeling heterogeneity in a manner that still represents the tumor of origin remains a formidable challenge. Sequencing technologies are limited in their ability to identify rare subclonal populations and predict response to treatments for patients. Patient-derived organotypic cultures have significantly improved the modeling of cancer biology by faithfully representing the molecular features of primary malignant tissues. Patient-derived cancer organoid (PCO) cultures contain subclonal populations with the potential to recapitulate heterogeneity, although treatment response assessments commonly ignore diversity in the molecular profile or treatment response. Here, we demonstrate the advantage of evaluating individual PCO heterogeneity to enhance the sensitivity of these assays for predicting clinical response. Additionally, organoid subcultures identify subclonal populations with altered treatment response. Finally, dose escalation studies of PCOs to targeted anti-EGFR therapy are utilized which reveal divergent pathway expression when compared to pretreatment cultures. Overall, these studies demonstrate the importance of population-based organoid response assessments, the use of PCOs to identify molecular heterogeneity not observed with bulk tumor sequencing, and PCO heterogeneity for understanding therapeutic resistance mechanisms.
Keywords: Clonal heterogeneity; Colorectal cancer; EGFR; Organoids; Targeted therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sato, T. et al. Long-term expansion of epithelial organoids from human colon, adenoma, adenocarcinoma, and Barrett’s epithelium. Gastroenterology141, 1762–1772 (2011). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

