RBM24 regulates apoptosis rates by modulating global transcriptome profile in CAL27 cells
- PMID: 40200085
- PMCID: PMC11978760
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-96932-5
RBM24 regulates apoptosis rates by modulating global transcriptome profile in CAL27 cells
Abstract
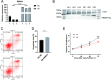
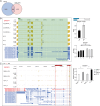
RNA binding proteins (RBPs) are key factors regulating post-transcriptional events. Categorized as RBPs, RBM24 expression levels have been shown to be a prognosis-related pivotal gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma. We analyzed the binding targets and regulated post-transcriptional events of RBM24 in RBM24-overexpressing cell lines and controls using iRIP-seq and RNA-seq. RBM24-overexpressing cells showed significant changes in gene expression, which are involved in biological pathways related to apoptosis and immune inflammation. RBM24-regulated genes that undergo alternative splicing are primarily engaged in biological processes related to DNA damage repair and RNA metabolism. More notably, we found that RBM24 binds to lncRNAs in addition to pre-mRNAs. These results indicated that RBM24 could play a key role in cancer progression by finding clinical therapeutic targets for Oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Keywords: Alternative splicing; Apoptosis; Cancer therapy; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; RBM24.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University and was performed according to the institutional guidelines.
Figures



References
-
- Gandini, S. et al. Tobacco smoking and cancer: a meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer122, 155–164 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Adil, N. et al. Evaluation of cytotoxicity of areca nut and its commercial products on normal human gingival fibroblast and oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. J. Hazard Mater403, 123872 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Miranda-Filho, A. & Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in cancers of the lip, tongue and mouth. Oral Oncol.102, 104551 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

