The induction effect of hydroxyurea and metformin on fetal globin in the K562 cell line
- PMID: 40200166
- PMCID: PMC11978054
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-025-01184-8
The induction effect of hydroxyurea and metformin on fetal globin in the K562 cell line
Abstract
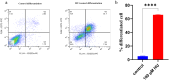
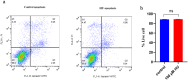
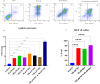
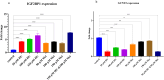
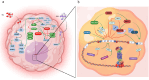
Despite the established efficacy of hydroxyurea (HU) in increasing fetal hemoglobin (Hb F) levels in patients with intermedia beta-thalassemia (β-thal) and sickle cell anemia, the precise molecular mechanisms underlying these effects remain largely elusive. Understanding these mechanisms is paramount for identifying alternative therapeutic approaches to increase Hb F production while minimizing adverse effects. In this study, we employed weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) to investigate the molecular underpinnings of γ-globin switching within GSE90878 dataset. Leveraging this information, we aimed to predict the transcriptome network and elucidate the mechanism of action of HU and Metformin (Met) on this network comprehensively. Through bioinformatic analysis, we identified IGF2BP1 and GCNT2 as key regulators of the γ-globin switching mechanism. To experimentally validate these findings, we utilized the K562 cell line as an erythroid model. Cells were treated with HU (50, 100, and 150 µM) and Met (50, 100, and 150 µM) for 24, 48, and 72 h. The expression levels of the GCNT2, γ-globin, IGF2BP1, miR-199a/b-5p, miR-451-5p and miR-144-3p were quantified using real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Our results revealed that treatment with HU (150 µM), Met (100 µM), and combination of HU-Met (150/100 µM) significantly increased IGF2BP1 expression by 6.2, 5.3, and 7.1-fold, respectively, after 24 h treatment. Furthermore, treatment with HU (50 µM), Met (50 µM) and HU/Met (50/50 µM) for 24 h led to a 3.3, 1.2, and 5-fold decrease in GCNT2 gene expression, respectively. Notably, the highest levels of γ-globin expression and Hb F production were observed with HU (100 µM), Met (50 µM), and HU/Met (100/50 µM). This study provides compelling evidence that HU and Met significantly enhance γ-globin expression and Hb F production in the K562 cell line. Our findings suggest that these drugs exert their effects by modulating the expression of IGF2BP1 and GCNT2, thus offering valuable insights into potential therapeutic strategies for disorders characterized by low Hb F levels.
Keywords: GCNT2; IGF2BP1; Beta-thalassemia; Hemoglobin F; Hydroxyurea; Metformin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: The study was approved by the ethics committee of Birjand University of Medical Sciences generated ethical acceptance (IR.BUMS.REC.1398.252). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Belmont A, Kwiatkowski JL. Deferiprone for the treatment of transfusional iron overload in thalassemia. Expert Rev Hematol. 2017;10(6):493–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

