Platelet-rich plasma and corticosteroid injection for tendinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40200209
- PMCID: PMC11980122
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-025-08566-3
Platelet-rich plasma and corticosteroid injection for tendinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we evaluated and compared the efficacy and safety of platelet-rich plasma injection into corticosteroid injection in the treatment of tendinopathy.
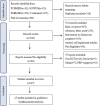
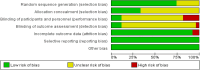
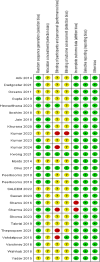
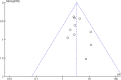
Methods: We searched PUBMED, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, SCOPUS, and Web of Science to identify randomized controlled trials on the PRP injection versus CS injection in treatment of tendinopathy.The meta-analysis was performed using the Revman 5.4 software.
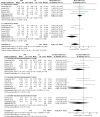
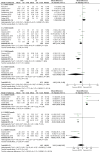
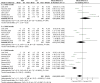
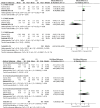
Result: We found 27 RCT studies with a total of 1779 patients enrolled. 8 rotator cuff injuries, 7 humeral external epicondylitis, 10 plantar fasciitis, and 2 tenosynovitis. The results of the meta-analysis showed that there were no significant group differences in the results of patients with rotator cuff injury comparing the pain visual analog scale score and functional measures at 1 month after receiving injection treatment. After three months of receiving PRP treatment, the VAS scores showed greater improvement compared to the CS group(OR = -1.64,95%CI [-2.97,-0.31],P = 0.02), while there was no statistically significant difference in shoulder joint function between the two groups at the 3-6 month post-treatment mark. Patients with plantar fasciitis showed no significant differences in VAS and AOFAS scores after receiving PRP or CS injections at 1 and 3 months. However, at the 6-month mark, the PRP group demonstrated significantly better VAS and AOFAS scores compared to the CS group(OR = -1.41,95%CI [-1.88,-0.44],P < 0.00001; OR = 7.19,95%CI [2.41,11.91],P = 0.003). 1 month after CS injection in patients with tenosynovitis, the VAS score was lower than that of the PRP group; patients with elbow epicondylitis had better improved upper limb function rating scale scores 1 month after CS injection compared to the PRP group. In patients with tenosynovitis, the VAS scores were superior to the CS group six months after PRP treatment(OR = -0.72,95%CI [-1.04,-0.40],P < 0.00001); similarly, patients with lateral epicondylitis exhibited better VAS, DASH scores than the CS group three and twelve months post-PRP treatment(OR = -9.76,95%CI [-10.89,-8.63],P = 0.0002; OR = -0.97,95%CI [-1.87,-0.06],P < 0.0001; OR = -18.03,95%CI [-31.61,-4.46],P = 0.009).
Conclusion: PRP can effectively improve pain and functional impairment in patients with tendinopathy, and its mid-term efficacy is superior to that of corticosteroids. However, the long-term efficacy remains to be further clinically verified.
Keywords: Corticosteroid; Meta-analysis; Platelet-rich plasma; Systematic review; Tendinopathies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Since our study is a meta-analysis, an Ethical Review Committee Statement is not required. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma in Patients With Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears or Tendinopathy Leads to Significantly Improved Short-Term Pain Relief and Function Compared With Corticosteroid Injection: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial.Arthroscopy. 2021 Feb;37(2):510-517. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2020.10.037. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Arthroscopy. 2021. PMID: 33127554 Clinical Trial.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection Can Be a Viable Alternative to Corticosteroid Injection for Conservative Treatment of Rotator Cuff Disease: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Arthroscopy. 2023 Feb;39(2):402-421.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2022.06.022. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Arthroscopy. 2023. PMID: 35810976 Review.
-
Subacromial injection of platelet-rich plasma provides greater improvement in pain and functional outcomes compared to corticosteroids at 1-year follow-up: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024 Dec;33(12):2563-2571. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2024.06.012. Epub 2024 Aug 3. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024. PMID: 39098382 Clinical Trial.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Has Better Results for Long-term Functional Improvement and Pain Relief for Lateral Epicondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Am J Sports Med. 2024 Aug;52(10):2646-2656. doi: 10.1177/03635465231213087. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Am J Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 38357713
-
Autologous growth factor injections in chronic tendinopathy.J Athl Train. 2014 May-Jun;49(3):428-30. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-49.3.06. Epub 2014 May 19. J Athl Train. 2014. PMID: 24840581 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gosens T, Peerbooms JC, van Laar W, den Oudsten BL. Ongoing positive effect of platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection in lateral epicondylitis: a double-blind randomized controlled trial with 2-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(6):1200–8. 10.1177/0363546510397173. - PubMed
-
- Monto RR. Platelet-rich plasma efficacy versus corticosteroid injection treatment for chronic severe plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;35(4):313–8. 10.1177/1071100713519778. - PubMed
-
- Malliaras P, Barton CJ, Reeves ND, Langberg H. Achilles and patellar tendinopathy loading programmes : a systematic review comparing clinical outcomes and identifying potential mechanisms for effectiveness. Sports Med. 2013;43(4):267–86. 10.1007/s40279-013-0019-z. - PubMed
-
- Krogh TP, Fredberg U, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Christensen R, Jensen P, Ellingsen T. Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with platelet-rich plasma, glucocorticoid, or saline: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(3):625–35. 10.1177/0363546512472975. - PubMed
-
- Millar NL, Silbernagel KG, Thorborg K, Kirwan PD, Galatz LM, Abrams GD, Murrell GAC, McInnes IB, Rodeo SA. Tendinopathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):1. 10.1038/s41572-020-00234-1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

