Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with MET alteration
- PMID: 40200811
- PMCID: PMC11976709
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0503
Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with MET alteration
Abstract
Alterations in the mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (MET) gene are critical drivers of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In recent years advances in precision therapies targeting MET alterations have significantly expanded treatment options for NSCLC patients. These alterations include MET exon 14 skipping mutations (MET exon 14 skipping), MET gene amplifications, MET point mutations (primarily kinase domain mutations), and MET protein overexpression. Accurate identification of these alterations and appropriate selection of patient populations and targeted therapies are essential for improving clinical outcomes. The East China Lung Cancer Group, Youth Committee (ECLUNG YOUNG, Yangtze River Delta Lung Cancer Cooperation Group) has synthesized insights from China's innovative drug development landscape and clinical practice to formulate an expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of NSCLC patients with MET alterations. This consensus addresses key areas, such as optimal testing timing, testing methods, testing strategies, quality control measures, and treatment approaches. By offering standardized recommendations, this guidance aims to streamline diagnostic and therapeutic processes and enhance clinical decision-making for NSCLC with MET alterations.
Keywords:
Copyright © 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
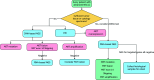
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:12–49. - PubMed
-
- Harshman LC, Choueiri TK. Targeting the hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer J. 2013;19:316–23. - PubMed
-
- Sakai K, Aoki S, Matsumoto K. Hepatocyte growth factor and Met in drug discovery. J Biochem. 2015;157:271–84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
