Comorbidities of overweight and obesity associated risk factor in Saudi Arabia: a population-based analysis
- PMID: 40200838
- PMCID: PMC11983525
- DOI: 10.1080/16549716.2025.2477387
Comorbidities of overweight and obesity associated risk factor in Saudi Arabia: a population-based analysis
Abstract
Background: Obesity is a significant public health challenge in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), with profound impacts on individual well-being and the healthcare system. Recent epidemiological studies have reported variable trends in obesity prevalence within the country. This population-based study aimed to estimate the prevalence, identify behavioral risk factors, and assess comorbidities associated with overweight and obesity using a nationally representative sample in KSA. Findings will inform targeted public health policies, optimize healthcare resource allocation, and support Saudi Vision 2030 goals by promoting healthier lifestyles and reducing chronic diseases.
Methods: This study analyzed data from the 2019 Kingdom of Saudi Arabia World Health Survey (KSAWHS), implemented by the Ministry of Health using a nationally representative sample. A stratified, three-stage sampling design based on the 2010 Census was used to select 10,000 households from 13 administrative regions. Data collection included socio-demographic, anthropometric measurements and medical information from consenting individuals. Continuous variables were summarized as mean ± SD, and univariate analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA and Chi-square tests. Logistic regression identified predictors of obesity and overweight, reporting odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Analyses were conducted in SPSS (v29).
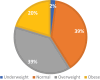
Results: A total of 7930 adults across different regions in KSA were included in this study. The overall prevalence of obesity and overweight was 20.3% and 38.7%, respectively. Overweight was significantly more prevalent in males (44.4%) than females (35.6%), whereas obesity was more common in females (22.1%) compared to males (18.6%) (p < 0.001). Regional differences were observed with the West region reporting the lowest prevalence of obesity (16.5%) and overweight (37.3%) (p < 0.001). Married individuals exhibited a significantly higher prevalence of both obesity and overweight (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The burden of obesity and overweight in KSA is still alarming due to the associated risk of metabolic, cardiovascular, and psychological disorders, affecting both patients and the healthcare system. Urgent interventions, including targeted public health campaigns, lifestyle modifications, and policy-driven strategies, are essential to curb obesity trends and promote long-term health improvements.
Keywords: Obesity; Saudi Arabia; overweight; prevalence; risk factors.
Plain language summary
Main findings: The prevalence of obesity and overweight in KSA was 20.3% and 38.7%, respectively, indicating a substantial public health burden. Obesity was significantly associated with metabolic, cardiovascular, and psychological disorders. Key behavioral risk factors included physical inactivity, poor dietary habits, and smoking.Added knowledge: Provides updated, nationally representative data on obesity trends and risk factors in KSA. Highlights the role of lifestyle behaviors in obesity prevalence and associated comorbidities. Identifies critical targets for intervention, emphasizing the need for evidence-based health strategies.Global health impact for policy and action: Supports the development of targeted public health policies to combat obesity-related diseases. Aligns with global efforts to reduce non-communicable diseases (NCDs) through preventive strategies. Reinforces the need for multi-sectoral approaches, including healthcare, education, and urban planning, to promote healthier lifestyles and reduce obesity rates.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Obesity and overweight: fact sheet. WHO Media Cent. 2016. June.
-
- World Obesity Federation . World obesity atlas 2023. 2023.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical