Muscle excitability testing: Age and sex dependency of normative data
- PMID: 40200982
- PMCID: PMC11978295
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cnp.2025.03.002
Muscle excitability testing: Age and sex dependency of normative data
Abstract
Objective: To establish normative data for muscle excitability testing in the tibialis anterior muscle of a healthy population, and to determine their dependence on age and sex.
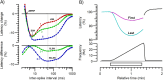
Methods: Parameters of muscle velocity recovery cycle recordings with 1, 2 and 5 conditioning stimuli of 197 healthy subjects and frequency ramp recordings of 151 healthy subjects were retrospectively analysed for age and sex differences.
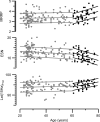
Results: There were no differences by sex and only small age differences were found in healthy subjects older than 60 years for the muscle excitability parameters muscle relative refractory period, early supernormality and latency to the first response in a train at 15 Hz and 30 Hz.
Conclusions: In this study, based on a large sample of muscle velocity recovery cycle and frequency ramp recordings, we have provided normative data and shown that muscle excitability testing is not influenced by sex, and that age only has an influence from the age of 60 years onwards on parameters reflecting muscle membrane potential.
Significance: Our results suggest that future studies no longer need to control for sex when using a healthy control group.
Keywords: Age; Direct muscle stimulation; Electric stimulation; Electromyography; Multi-fibre muscle velocity recovery cycle; Sarcolemmal excitability properties.
Crown Copyright © 2025 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: [Hugh Bostock and James Howells receive from UCL shares of the royalties for sales of the Qtrac software. The other authors have no potential conflicts of interest to declare.].
Figures

References
-
- Bae J.S., Sawai S., Misawa S., Kanai K., Isose S., Shibuya K., et al. Effects of age on excitability properties in human motor axons. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008;119(10):2282–2286. - PubMed
-
- Boërio D., Z'Graggen W.J., Tan S.V., Guetg A., Ackermann K., Bostock H. Muscle velocity recovery cycles: effects of repetitive stimulation on two muscles. Muscle Nerve. 2012;46(1):102–111. - PubMed
-
- Boland-Freitas R., Lee J.H., Ng K. Serum electrolyte concentrations and skeletal muscle excitability in vivo. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022;135:13–21. - PubMed
-
- Bostock H., Baumann C., Humm A.M., Z'Graggen W.J. Temperature dependency of human muscle velocity recovery cycles. Muscle Nerve. 2012;46(2):264–266. - PubMed
-
- Jankelowitz S.K., McNulty P.A., Burke D. Changes in measures of motor axon excitability with age. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007;118(6):1397–1404. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

