Syntheses and crystal structures of three tri-phenyl-sulfonium halometallate salts of zinc, cadmium and mercury
- PMID: 40201007
- PMCID: PMC11974339
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025002245
Syntheses and crystal structures of three tri-phenyl-sulfonium halometallate salts of zinc, cadmium and mercury
Abstract
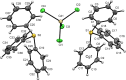
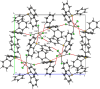
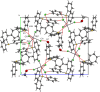
Bis(tri-phenyl-sulfonium) tetra-chlorido-zinc(II), (C18H15S)2[ZnCl4] (I), bis-(tri-phenyl-sulfonium) tetra-chlorido-cadmium(II), (C18H15S)2[CdCl4] (II), and bis-(tri-phenyl-sulfonium) tetra-chlorido-mercury(II) methanol monosolvate, (C18H15S)2[HgCl4]·CH3OH (III), each crystallize in the monoclinic space group P21/n. In all three structures, there are two crystallographically independent tri-phenyl-sulfonium (TPS) cations per asymmetric unit, each adopting a distorted trigonal-pyramidal geometry about the S atom (S-C bond lengths in the 1.77-1.80 Å range and C-S-C angles of 100-107°). The [MCl4]2- anions (M = Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+) are tetra-hedral; their M-Cl bond lengths systematically increase from Zn2+ to Hg2+, consistent with the larger ionic radius of the heavier metal. Hirshfeld surface analyses show that H⋯H and H⋯C contacts dominate the TPS cation environments, whereas H⋯Cl and S⋯M inter-actions anchor each [MCl4]2- anion to two surrounding TPS cations. Weak C-H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds, as well as inversion-centered π-π stacking, generate layers in (I) and (II) and dimeric [(TPS)2-HgCl4]2 assemblies in (III).
Keywords: crystal structure; salts; triphenylsulfonium ion.
© Artis et al. 2025.
Figures



References
-
- Barrett, J. N., Barrett, D. F. & Ingber, L. (1976). Biochem. J.15, 1512–1516.
-
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst.42, 339–341.
-
- Klapötke, T. M. & Krumm, B. (2009a). Z. Naturforsch. B Chem. Sci.64, 467–469.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
