Rituximab treatment in Chinese patients with primary angiitis of the central nervous system
- PMID: 40201016
- PMCID: PMC11977535
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1554989
Rituximab treatment in Chinese patients with primary angiitis of the central nervous system
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the efficacy and safety of rituximab (RTX) in Chinese patients with primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS).
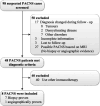
Methods: Herein, we present the outcomes of 8 patients who received RTX for PACNS. Seven patients underwent a brain biopsy showing vasculitis, while the remaining patient had a digital subtraction angiogram and clinical findings highly suggestive of vasculitis. Clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging modalities were performed during the initial RTX administration and follow-up. The Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) disability score was used to assess treatment response and degree of disability.
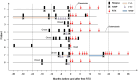
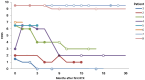
Results: The median age at diagnosis of the 8 patients (2 females) was 37.0 years. All patients had active disease when RTX treatment was initiated. Five of the eight patients had refractory disease, and received one or more conventional immunosuppressants (IS). Three patients had contraindications or refused conventional IS. Patients were followed up until their death or the final follow-up visit (median 18 months; range: 0-40 months). The median EDSS score at the last visit (median 3.0; range 0-9.5) was lower than before RTX administration (median 6.5; range 1.5-9.5). In 6 patients, RTX administration was associated with a marked reduction in the number of flare-ups. Two of the six patients developed infections: one with pneumonia, and the other with tuberculosis. In one patient, parenchymal gadolinium enhancement persisted, and a new lesion was found following three courses of RTX.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that RTX therapy may be an additional treatment option for Chinese patients with PACNS.
Keywords: PACNS; PCNSV; primary angiitis of the central nervous system; rituximab; vasculitis.
Copyright © 2025 Wei, Wang, Yin, Guo, Zhang, Sun, Lu, Zhang and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Salvarani C, Brown RD, Jr, Christianson T, Miller DV, Giannini C, Huston J, 3rd, et al. . An update of the Mayo Clinic cohort of patients with adult primary central nervous system vasculitis: description of 163 patients. Medicine. (2015) 94:e738. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000738, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Boysson H, Zuber M, Naggara O, Neau JP, Gray F, Bousser MG, et al. . Primary angiitis of the central nervous system: description of the first fifty-two adults enrolled in the French cohort of patients with primary vasculitis of the central nervous system. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2014) 66:1315–26. doi: 10.1002/art.38340, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

