Shadows of the bleeding joint: A radiologic exploration
- PMID: 40201053
- PMCID: PMC11978294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2025.02.089
Shadows of the bleeding joint: A radiologic exploration
Abstract
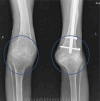
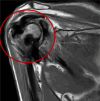
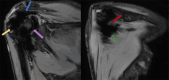
Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that manifests due to a deficiency of clotting factors. One of the most common complications is hemophilic arthropathy which results in bleeding into large joints causing hemosiderin deposition. Recurrent hemarthrosis causes joint destruction resulting in pain and a decreased range of movements. Radiological imaging is essential for staging, prognostication, and treatment protocol. X-rays show the extent of joint destruction and narrowing of joint space. Ultrasonography helps in visualizing tendons and joint effusion. However magnetic resonance imaging is the gold standard for staging hemophilic arthropathy. Management involves both medical and surgical intervention as per the level of joint involvement.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Clotting; Hemarthrosis; Hemophilia; Osteoarthritis.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures




References
-
- Kaur R., Dahuja A., Singh P., Aggarwal S. Hemophilic arthropathy of the knee: a case report with discussion on the role of imaging with review of literature. J Clin Sci. 2019;16:101–104.
-
- Stephensen D., Tait R.C., Brodie N., Collins P., Cheal R., Keeling D., et al. Changing patterns of bleeding in patients with severe haemophilia A. Haemophilia. 2009;15(6):1210–1214. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

