Spatial transcriptomics delineates potential differences in intestinal phenotypes of cardiac and classical necrotizing enterocolitis
- PMID: 40201118
- PMCID: PMC11978348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112166
Spatial transcriptomics delineates potential differences in intestinal phenotypes of cardiac and classical necrotizing enterocolitis
Abstract
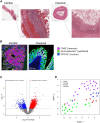
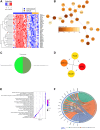
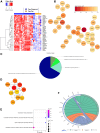
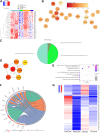
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating neonatal gastrointestinal disease, often resulting in multi-organ failure and death. While classical NEC is strictly associated with prematurity, cardiac NEC is a subset of the disease occurring in infants with comorbid congenital heart disease. Despite similar symptomatology, the NEC subtypes vary slightly in presentation and may represent etiologically distinct diseases. We compared ileal spatial transcriptomes of patients with cardiac and classical NEC. Epithelial and immune cells cluster well by cell-type segment and NEC subtype. Differences in metabolism and immune cell activation functionally differentiate the cell-type makeup of the NEC subtypes. The classical NEC phenotype is defined by dysbiosis-induced inflammatory signaling and metabolic acidosis, while that of cardiac NEC involves reduced angiogenesis and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Despite subtype-associated clinical and demographic variability, spatial transcriptomics has substantiated pathway and network differences within immune and epithelial segments between cardiac and classical NEC.
Keywords: Components of the immune system; Disease; Gastroenterology; Pediatrics; Proteomics; Transcriptomics.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
H.C. is a scientific advisory board member for the NEC Society (501c-3).
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

