Human Schwann Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Isolation, Bioactivity Assessment, and Omics Characterization
- PMID: 40201152
- PMCID: PMC11977562
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S500159
Human Schwann Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Isolation, Bioactivity Assessment, and Omics Characterization
Abstract
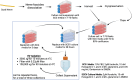
Purpose: Schwann cell-derived extracellular vesicles (SCEVs) have demonstrated favorable effects in spinal cord, peripheral nerve, and brain injuries. Herein, a scalable, standardized, and efficient isolation methodology of SCEVs obtaining a high yield with a consistent composition as measured by proteomic, lipidomic, and miRNA analysis of their content is described for future clinical use.
Methods: Human Schwann cells were obtained ethically from nine donors and cultured in a defined growth medium optimized for proliferation. At confluency, the culture was replenished with an isolation medium for 48 hours, then collected and centrifuged sequentially at low and ultra-high speeds to collect purified EVs. The EVs were characterized with mass spectrometry to identify and quantify proteins, lipidomic analysis to assess lipid composition, and next-generation sequencing to confirm miRNA profiles. Each batch of EVs was assessed to ensure their therapeutic potential in promoting neurite outgrowth and cell survival.
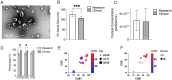
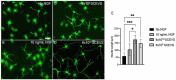
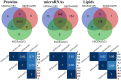
Results: High yields of SCEVs were consistently obtained with similar comprehensive molecular profiles across samples, indicating the reproducibility and reliability of the isolation method. Bioactivity to increase neurite process growth was confirmed in vitro. The predominance of triacylglycerol and phosphatidylcholine suggested its role in cellular membrane dynamics essential for axon regeneration and inflammation mitigation. Of the 2517 identified proteins, 136 were closely related to nervous system repair and regeneration. A total of 732 miRNAs were cataloged, with the top 30 miRNAs potentially contributing to axon growth, neuroprotection, myelination, angiogenesis, the attenuation of neuroinflammation, and key signaling pathways such as VEGFA-VEGFR2 and PI3K-Akt signaling, which are crucial for nervous system repair.
Conclusion: The study establishes a robust framework for SCEV isolation and their comprehensive characterization, which is consistent with their therapeutic potential in neurological applications. This work provides a valuable proteomic, lipidomic, and miRNA dataset to inform future advancements in applying SCEV to the experimental treatment of neurological injuries and diseases.
Keywords: axon growth; lipidomic; myelination; neuroprotection; regeneration.
© 2025 Khan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts related to this paper.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

