CTHRC1: a key player in colorectal cancer progression and immune evasion
- PMID: 40201173
- PMCID: PMC11975584
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1579661
CTHRC1: a key player in colorectal cancer progression and immune evasion
Abstract
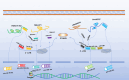
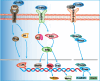
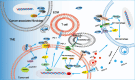
The multifunctional secreted protein, collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 (CTHRC1), has recently emerged as a significant focus within oncology research. CTHRC1 expression in tumors is governed by a complex interplay of regulatory signals, including methylation, glycosylation, and notably, non-coding RNAs, which constitute its predominant regulatory mechanism. Colorectal cancer (CRC), a highly prevalent epithelial malignancy, sees CTHRC1 influencing tumor progression and metastasis through its modulation of several downstream signaling cascades, such as Wnt/PCP, TGF-β/Smad, and MEK/ERK pathways. Furthermore, CTHRC1 contributes to immune evasion in CRC via diverse mechanisms. It is intricately associated with macrophage phenotypic switching within the tumor microenvironment (TME), favoring M2 macrophage polarization and facilitating the infiltration of T cells and neutrophils. CTHRC1 is also instrumental in immune escape by driving the remodeling of the extracellular matrix through interactions with cancer-associated fibroblasts. Additionally, CTHRC1's roles extend to the regulation of hypoxia-related pathways, metabolism of glycolysis and fatty acids, and involvement in tumor angiogenesis, all of which support tumor immune evasion. Considering its multifaceted activities, CTHRC1 emerges as a promising therapeutic target in CRC, with the potential to enhance the outcomes of existing radiotherapeutic and immunotherapeutic regimens. This review endeavors to delineate the mechanistic and therapeutic landscapes of CTHRC1 in CRC. Through a comprehensive discussion of CTHRC1's diverse functions, we aim to provide insights that could pave the way for innovative approaches in cancer therapy.
Keywords: CTHRC1; colorectal cancer; immune evasion; progression; therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Wang, Liu and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pyagay P, Heroult M, Wang Q, Lehnert W, Belden J, Liaw L, et al. Collagen triple helix repeat containing 1, a novel secreted protein in injured and diseased arteries, inhibits collagen expression and promotes cell migration. Circ Res. (2005) 96:261–8. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000154262.07264.12 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

