Blood pressure impact of dietary practices using the DASH method: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40201316
- PMCID: PMC11975635
- DOI: 10.5646/ch.2025.31.e12
Blood pressure impact of dietary practices using the DASH method: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: In order to ascertain the impact of the Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet on blood pressure (BP), a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials were carried out. DASH is advised for lowering BP.
Methods: Scopus databases were searched from the beginning of 2024. A total of 579 articles from 2019 to 2023 from PubMed: 15, Scopus: 164 and Crossref: 400. There were 8 articles included in the meta-analysis.
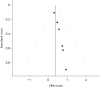
Results: Systolic BP (1.29 mmHg to 4.6 mmHg, 95% CI, -2.17, -0.41; P < 0.005) and diastolic BP (0.76 mmHg to 1.1 mmHg, 95% CI, -1.39, -0.13; P < 0.005) were found to be significantly reduced by the DASH diet, while total cholesterol concentrations (5.2 mmol/L; P < 0.005), low-density lipoprotein (8.2 mmol/L; P = 0.03), and high-density lipoprotein increased by 8.2% (P < 0.005) were lowered by 0.9 points.
Conclusions: When followed consistently, the DASH diet can reduce BP's systolic and diastolic readings.
Trial registration: PROSPERO Identifier: CRD42023494005.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Dietary behavior; Reduced.
Copyright © 2025 The Korean Society of Hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bonekamp NE, Cruijsen E, Visseren FL, van der Schouw YT, Geleijnse JM, Koopal C. Compliance with the DASH diet and risk of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with myocardial infarction. Clin Nutr. 2023;42:1418–1426. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources