Evaluation of PDZD11 in hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic value and diagnostic potential in combination with AFP
- PMID: 40201341
- PMCID: PMC11975663
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1533865
Evaluation of PDZD11 in hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic value and diagnostic potential in combination with AFP
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most prevalent liver cancer, with a 5-year survival rate below 20% and an average survival time of 3-6 months. Identifying new biomarkers is crucial for early diagnosis and prognosis. The function of PDZ domain protein 11 (PDZD11) in HCC remains unclear.
Methods: In this study, PDZD11 was investigated as a potential biomarker for HCC using bioinformatic analysis of the TCGA and ICGC datasets. Furthermore, we assessed the potential of serum PDZD11 as a clinical diagnostic marker by enrolling a cohort comprising 78 HCC patients and 62 healthy controls (HC) using the ELISA analysis and combining its expression with common tumor markers.
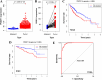
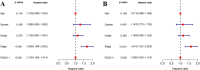
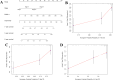
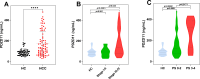
Results: Our research found significantly higher PDZD11 mRNA expression in HCC tissues compared to tumor-adjacent tissues (p < 0.001), which was associated with lower overall survival (OS) rates (p < 0.01). Multivariate evaluation methods established PDZD11 as a standalone predictor of prognosis. A nomogram incorporating PDZD11 expression and clinicopathological factors predicted OS rates for HCC patients over various years. Patients with HCC exhibited notably elevated serum PDZD11 levels compared to HC, with these levels rising further in advanced disease stages and deteriorating performance status (PS). ROC analysis showed high diagnostic accuracy when PDZD11 is combined with AFP (AUC = 0.958).
Conclusion: PDZD11 is more sensitive than AFP in assessing HCC prognosis. In conclusion, PDZD11 is a promising supplementary biomarker for HCC diagnosis and prognosis alongside AFP.
Keywords: AFP; PDZD11; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognosis; serological biomarker.
Copyright © 2025 Ni, Liu, Zhang, Pang, Tian, Lv, Shi, Zheng and Fan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

