Macrophage Changes and High-Throughput Sequencing in Aging Mouse Intervertebral Disks
- PMID: 40201536
- PMCID: PMC11977178
- DOI: 10.1002/jsp2.70061
Macrophage Changes and High-Throughput Sequencing in Aging Mouse Intervertebral Disks
Abstract
Background: Intervertebral disk (IVD) degeneration is associated with lower back pain and aging; however, the mechanisms underlying age-related changes and the changes in macrophage polarization in aging intervertebral disks require further elucidation. The aim of this study was to evaluate changes in macrophages, the differential expression of senescence genes, and their relationship with hub genes in IVDs during aging in mice.
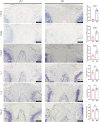
Methods: Twenty-eight male wild C57 mice aged 4 weeks were divided into two groups. Four mice per group were selected for high-throughput sequencing and 10 for tail IVD immunohistochemical analysis. Adult and aged mouse IVD specimens were stained with hematoxylin-eosin, Fast Green, and Alcian Blue to determine collagen (Col) 1, Col2, proteoglycan, P16, P21, P53, CD11b, CD86, CD206, IL-1, TGF-β, and IL-4 expression. High-throughput sequencing was performed on adult and aged mouse IVD tissues.
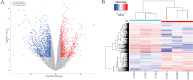
Results: Aged mouse IVDs showed reduced height and marked degeneration, with decreased Col2 and proteoglycan expression and increased Col1 expression. The expression of senescence markers, senescence-associated IL-1, TGF-β, and IL-4, and macrophage-related markers, CD11b, CD86, and CD206, increased markedly with age. High-throughput sequencing revealed 1975 differentially expressed genes in adult and aged mice, with 797 genes showing upregulated expression (top five: Kcna7, Mmp9, Panx3, Myl10, and Bglap) and 1178 showing downregulated expression (top five: Srd5a2, Slc38a5, Gm47283, Npy, and Pcdh8). Gene Ontology and pathway enrichment analyses highlighted aging-related cellular components, biological processes, and metabolic pathways. The identified hub genes included Cox5a, Ndufs6, and Ndufb9.
Conclusions: Disk senescence and reduced height in aged mice are linked to upregulated expression of senescence-associated phenotypes and macrophage polarization markers. These findings suggest that macrophages and differential gene expression play key roles in age-related IVD degeneration, indicating that they can be used as potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: high‐throughput sequencing; intervertebral disk; macrophages; senescence.
© 2025 The Author(s). JOR Spine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Orthopaedic Research Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators , “Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived With Disability for 301 Acute and Chronic Diseases and Injuries in 188 Countries, 1990–2013: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013,” Lancet 386, no. 10159 (2015): 743–800, 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

