Genetic analysis reveals the shared genetic architecture between breast cancer and atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 40201568
- PMCID: PMC11975938
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1450259
Genetic analysis reveals the shared genetic architecture between breast cancer and atrial fibrillation
Abstract
Background: Epidemiological studies have observed an association between atrial fibrillation (AF) and breast cancer (BC). However, the underlying mechanisms linking these two conditions remain unclear. This study aims to systematically explore the genetic association between AF and BC.
Methods: We utilized the largest available genome-wide association study (GWAS) datasets for European individuals, including summary data for AF (N = 1,030,836) and BC (N = 247,173). Multiple approaches were employed to systematically investigate the genetic relationship between AF and BC from the perspectives of pleiotropy and causality.
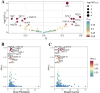
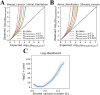
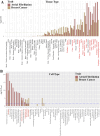
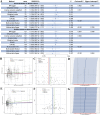
Results: Global genetic analysis using LDSC and HDL revealed a genetic correlation between AF and BC (rg = 0.0435, P = 0.039). Mixer predicted genetic overlap between non-MHC regions of the two conditions (n = 125, rg = 0.05). Local genetic analyses using LAVA and GWAS-PW identified 22 regions with potential genetic sharing. Cross-trait meta-analysis by CPASSOC identified one novel pleiotropic SNP and 14 pleiotropic SNPs, which were subsequently annotated. Eight of these SNPs passed Bayesian colocalization tests, including one novel pleiotropic SNP. Further fine-mapping analysis identified a set of causal SNPs for each significant SNP. TWAS analyses using JTI and FOCUS models jointly identified 10 pleiotropic genes. Phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) of novel pleiotropic SNPs identified two eQTLs (PELO, ITGA1). Gene-based PheWAS results showed strong associations with BMI, height, and educational attainment. PCGA methods combining GTEx V8 tissue data and single-cell RNA data identified 16 co-enriched tissue types (including cardiovascular, reproductive, and digestive systems) and 5 cell types (including macrophages and smooth muscle cells). Finally, univariable and multivariable bidirectional Mendelian randomization analyses excluded a causal relationship between AF and BC.
Conclusion: This study systematically investigated the shared genetic overlap between AF and BC. Several pleiotropic SNPs and genes were identified, and co-enriched tissue and cell types were revealed. The findings highlight common mechanisms from a genetic perspective rather than a causal relationship. This study provides new insights into the AF-BC association and suggests potential experimental targets and directions for future research. Additionally, the results underscore the importance of monitoring the potential risk of one disease in patients diagnosed with the other.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; breast cancer; causal inference; genetic correlation; pleiotropic gene; shared genetic etiology.
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Chen, Zhao, Gong, Liu, Miao, Lin, Ge and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aune D., Sen A., Schlesinger S., Norat T., Janszky I., Romundstad P., et al. (2017). Body mass index, abdominal fatness, fat mass and the risk of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 32, 181–192. 10.1007/s10654-017-0232-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

