Transforming cancer treatment: integrating patient-derived organoids and CRISPR screening for precision medicine
- PMID: 40201690
- PMCID: PMC11975957
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1563198
Transforming cancer treatment: integrating patient-derived organoids and CRISPR screening for precision medicine
Abstract
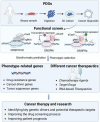
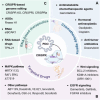
The persistently high mortality rates associated with cancer underscore the imperative need for innovative, efficacious, and safer therapeutic agents, as well as a more nuanced understanding of tumor biology. Patient-derived organoids (PDOs) have emerged as innovative preclinical models with significant translational potential, capable of accurately recapitulating the structural, functional, and heterogeneous characteristics of primary tumors. When integrated with cutting-edge genomic tools such as CRISPR, PDOs provide a powerful platform for identifying cancer driver genes and novel therapeutic targets. This comprehensive review delves into recent advancements in CRISPR-mediated functional screens leveraging PDOs across diverse cancer types, highlighting their pivotal role in high-throughput functional genomics and tumor microenvironment (TME) modeling. Furthermore, this review highlights the synergistic potential of integrating PDOs with CRISPR screens in cancer immunotherapy, focusing on uncovering immune evasion mechanisms and improving the efficacy of immunotherapeutic approaches. Together, these cutting-edge technologies offer significant promise for advancing precision oncology.
Keywords: CRISPR screening; cancer treatment; immunotherapy; patient-derived organoids; precision medicine.
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Shen, Ho, Hu, Ma and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

