The effect of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) on the number of glial cells in white rats (Rattus norvegicus) exposed to cigarette smoke
- PMID: 40201823
- PMCID: PMC11974293
- DOI: 10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i2.19
The effect of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) on the number of glial cells in white rats (Rattus norvegicus) exposed to cigarette smoke
Abstract
Background: Cigarette smoke is known to have harmful effects on the brain, particularly on glial cells, which play a crucial role in maintaining the health and functionality of the central nervous system. Nigella sativa (black cumin) has been reported to have neuroprotective properties, but its effects on glial cells in the cerebellum and cerebrum when exposed to cigarette smoke are not well understood.
Aim: This study aimed to determine the benefits of N. sativa on the number of glial cells in the cerebellum and cerebrum of white rats (Rattus norvegicus) exposed to cigarette smoke.
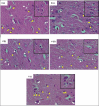
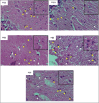
Methods: Thirty white rats weighing approximately 105 g were divided into five groups: K (control group, no exposure to cigarette smoke and without given N. sativa), K+ (exposed to cigarette smoke, 2 cigarettes/day, and 0.5% CMC), and three treatment groups (P1, P2, and P3) exposed to cigarette smoke, 2 cigarettes/day, with N. sativa dosages of 300, 600, and 1200 mg/kg BW, respectively. The number of glial cells in the cerebellum and cerebrum was examined under a microscope at 400x magnification. Data were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA test, followed by the post hoc Duncan test.
Results: Significant difference (p < 0.05) in the number of glial cells in both the cerebellum and cerebrum between the control and treatment groups.
Conclusion: The administration of N. sativa, particularly at a dosage of 1,200 mg/kg BW/day, significantly increased and maintained the number of glial cells in the cerebellum and cerebrum of rats exposed to cigarette smoke.
Keywords: Cerebellum; Cerebrum; Cigarette smoke; Good health and well-being; Nigella sativa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
