The role of veterinary drug use in driving antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolates in smallholder swine farms in Central Vietnam
- PMID: 40201839
- PMCID: PMC11974315
- DOI: 10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i2.34
The role of veterinary drug use in driving antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolates in smallholder swine farms in Central Vietnam
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus is a well-known opportunistic pathogen widely present in humans and food- producing animals. The emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in S. aureus represents a major challenge to animal and public health. Poor biosecurity practices and the misuse and overuse of veterinary drugs in farming settings may apply environmental pressure, which favors the selection of AMR bacteria.
Aim: This study aimed to describe veterinary drug usage (VDU), prevalence of AMR phenotypes, and associations among S. aureus isolates from swine of smallholder farms in Central Vietnam.
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted to collect VDU data from smallholder swine farms. A total of 155 nasal swab samples were collected and used for isolating S. aureus. The AMR of S. aureus strains was tested using the disk diffusion method.
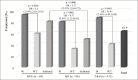
Results: Approximately 56.8%, 71.6%, 36.1%, and 69.7% of farmers used vaccines, disinfectants, and antimicrobials (AMs) for prevention and treatment, respectively. Of the 155 nasal swab samples, 99 (63.9%) were positive for S. aureus. Resistance was most commonly observed against oxacillin (59.6%), cefotaxime (59.6%), and linezolid (53.5%). Positive associations were found between the use of vaccines and resistance to oxytetracycline (OR = 3.28, p = 0.01) and povidone usage and resistance to meropenem (OR = 9.35, p = 0.03). Almost all positive associations were observed between the use of AMs (for both prevention and treatment) and AMR in S. aureus. Negative associations were found between resistance to oxytetracycline and the use of gentamicin, linezolid, streptomycin, and norfloxacin.
Conclusion: The present study highlights information on VDU, prevalence, AMR, and their associations with S. aureus isolated from a smallholder swine farm in Central Vietnam. These findings are expected to aid in developing countermeasures against AMR against swine production in Vietnam.
Keywords: Antimicrobial; Disinfectant; Resistance; Staphylococcus aureus; Swine; Vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding any financial, personal, or other relationships with individuals or organizations related to the material discussed in this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Asai T., Kojima A., Harada K., Ishihara K., Takahashi T., Tamura Y. Correlation between the usage volume of veterinary therapeutic antimicrobials and resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from the feces of food-producing animals in Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2005;58(6):369–372. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical