Morphological examination of the normal kidney and urinary bladder in goats (Capra hircus) using anatomical sections and computed tomography
- PMID: 40201853
- PMCID: PMC11974314
- DOI: 10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i2.31
Morphological examination of the normal kidney and urinary bladder in goats (Capra hircus) using anatomical sections and computed tomography
Abstract
Background: Cross-sectional imaging is set to become the standard method for diagnosing various pathological conditions of the urinary tract in goats, and the concept for this atlas originated from this understanding. Until now, there has not been a comprehensive comparative atlas detailing the structures of the urinary tract in goats and their relationships with other organs.
Aim: The main aim and objective of this study was to compare anatomically frozen cross-sections and detailed computed tomography (CT) images of the urinary tract, which may be used to diagnose urinary abnormalities and affections in goats.
Methods: Eight healthy adult goats (Capra hircus) of both sexes were collected for anatomical and diagnostic examinations; average age: 15-25 ± 0.52 months and average weight: 25-35 ± 0.42 kg. The study focused on the pelvic and abdominal cavities, along with their contents and relationship with urinary organs. The examination included the analysis of bony and soft tissues using median, sagittal, and cross-anatomical sections. Subsequently, the specimens were subjected to diagnostic screening by CT.
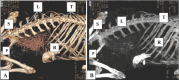
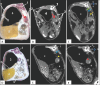
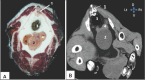
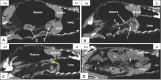
Results: We found that both kidneys were readily distinguishable in both anatomical and CT scans as spherical to bean-shaped, but in the CT scan, the kidneys exhibited hypoechoic features with an anechoic hilus, and there was no sharp demarcation between the cortex and medulla, although the cortex was slightly denser than the medulla. In the dorsal-plane CT scan, the right ureter was positioned dorsally adjacent to the caudal vena cava, extending toward the urinary bladder. The egress of the left ureter from the left renal hilus was observed in the transverse CT image. On transverse- and dorsal plane CT, the urinary bladder may be identified at the sacrum level on the pelvic floor, located beneath the uterus and rectum. A dorsal-plane CT scan revealed the presence of the urethra exiting the urine bladder in a caudal direction.
Conclusion: The cross-sectional layout of CT images enables both students and clinicians to observe the anatomical connections and features of the goat urinary tract, which might not be easily seen through dissection alone. Furthermore, this atlas could serve as a helpful resource for study and clinical reference to enhance the understanding of goat urinary tract anatomy, which can ultimately help address pathological conditions.
Keywords: CT; Frozen cross sections; Goat; Urinary bladder; kidney.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that we do not have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Alnahrawy E.H, Rashed R, Shogy K, Erasha A. Morphological and diagnostic imaging studies on pelvic cavity of Egyptian female baladi goat (Capra hircus) J. Cur. Vet. Res. 2021;3:32–40.
-
- Alsafy M, El-Gendy S, El-kammar M.H, Ismaiel M. Contrast radiographic, ultrasonographic and computed tomographic imaging studies on the abdominal organs and fatty liver infiltration of zaraibigoat. J. Med. Sci. 2013;13:316–326.
-
- Braun J, Van Den Berg R, Baraliakos X, Boehm H, Burgos-Vargas R, Collantes-Estevez E, Dagfinrud H, Dijkmans B, Dougados M, Emery P, Geher P, Hammoudeh M, Inman R.D, Jongkees M, Khan M.A, Kiltz U, Kvien T.K, Leirisalo-Repo M, Maksymowych W.P, Olivieri I, Pavelka K, Sieper J, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Wendling D, Özgocmen S, Van Drogen C, Van Royen B.J, Van Der Heijde D. Update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rhe. Dis. 2010;70(6):896–904. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Braun U, Irmer M, Augsburger H, Ohlerth S. Computed tomography of the abdomen in saanen goats: III. Kidneys, ureters and urinary bladder. Schw. Archiv. Fur Tie. 2011;153:321–329. - PubMed
-
- Braun U, Schnetzler C, Augsburger H, Bettschart W, Ohlerth S. Computed tomography of the abdomen of calves during the first 105 days of life: III. Urinary tract and adrenal glands. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2014;156:237–247. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
