Papilledema With Intracranial Hypertension and Ectopic Orbital Calcification During Hemodialysis: A Case Report
- PMID: 40201865
- PMCID: PMC11977438
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.80284
Papilledema With Intracranial Hypertension and Ectopic Orbital Calcification During Hemodialysis: A Case Report
Abstract
Papilledema is optic disc swelling due to intracranial hypertension, which leads to progressive visual impairment. We report a rare case of papilledema with ectopic orbital calcification during hemodialysis. A 34-year-old woman with low body weight who was undergoing long-term hemodialysis presented with papilledema in both eyes, and her vision gradually deteriorated over the course of six months. The best corrected visual acuity was 20/16 in the right eye and 20/500 in the left eye, and fundus examination revealed significant optic disc swelling and visual field testing revealed nasal defects in both eyes and a central scotoma in the left eye. Computed tomography scan showed ectopic orbital calcification in the sclera and optic nerve margin. Orbital magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance venography did not show optic neuritis or cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Blood test results indicated hyperparathyroidism, which was considered to be a secondary change associated with long-term hemodialysis. Cerebrospinal fluid test confirmed intracranial hypertension, and treatment to reduce intracranial pressure was required to prevent the progression of visual impairment. Oral treatment was difficult, so surgical treatment was considered. Papilledema can be diagnosed from optic disc findings, and it is important to differentiate and search for various causes, including idiopathic intracranial hypertension, and to intervene at the appropriate time before visual impairment progresses.
Keywords: cerebrospinal pressure shunt surgery; ectopic calcification; intracranial hypertention; optic disc swelling; papilledema.
Copyright © 2025, Takahashi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
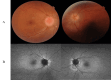

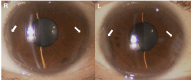


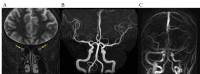

References
-
- Papilledema: a review of etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Xie JS, Donaldson L, Margolin E. Surv Ophthalmol. 2022;67:1135–1159. - PubMed
-
- Sclerochoroidal calcification: clinical features, outcomes, and relationship with hypercalcemia and parathyroid adenoma in 179 eyes. Shields CL, Hasanreisoglu M, Saktanasate J, Shields PW, Seibel I, Shields JA. Retina. 2015;35:547–554. - PubMed
-
- Optic nerve sheath calcification. Isen DR, Gaddamanugu S, Kline LB. Ophthalmology. 2023;130:204. - PubMed
-
- Ischemic optic neuropathy in dialyzed patients: a previously unrecognized manifestation of calcific uremic arteriolopathy. Korzets A, Marashek I, Schwartz A, Rosenblatt I, Herman M, Ori Y. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;44:0–7. - PubMed
-
- Calciphylaxis and bilateral optic neuropathy. Huerva V, Sánchez MC, Ascaso FJ, Craver L, Fernández E. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2011;34:651–654. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
