TRPC4 Mediates Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain via Ca2+-ERK/P38-ATF2 Pathway in the Trigeminal Ganglion of Mice
- PMID: 40202077
- PMCID: PMC11979714
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.70368
TRPC4 Mediates Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain via Ca2+-ERK/P38-ATF2 Pathway in the Trigeminal Ganglion of Mice
Abstract
Background: Trigeminal neuropathic pain (TNP) is a debilitating condition characterized by chronic facial pain, yet its underlying mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Transient Receptor Potential Canonical 4 (TRPC4) has been reported to promote the development of abnormal pain or pain hypersensitivity in neuropathic pain. However, the specific contribution of TRPC4 to TNP pathogenesis remains unclear.
Aim: This study aimed to investigate the role of TRPC4 in a mouse model of trigeminal neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction of the unilateral infraorbital nerve (CION).
Methods: Adult male/female mice were subjected to either CION surgery or sham surgery. Behavioral assays were conducted to assess facial pain-like responses over a 28-day period. TRPC4 distribution in the trigeminal ganglion (TG) was evaluated using Immunofluorescence. TRPC4 inhibitor ML204 and agonist Englerin A were employed to evaluate the impact of TRPC4 on facial pain-like behaviors. A TRPC4-overexpressing HEK293 cell model was conducted via plasmid transfection. To assess the function of TRPC4, we employed cellular calcium imaging technology to investigate the effects of modulating TRPC4 function by analyzing dynamic changes in intracellular calcium ion concentrations in primary trigeminal ganglion neurons and HEK293 cells. Trpc4 shRNA was used to specifically knock down TRPC4 in the trigeminal ganglion. Western blot analysis was used to assess the activation of ERK, P38, and ATF2 signaling pathways.
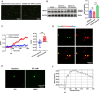
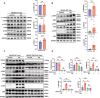
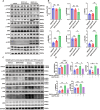
Results: Mice subjected to CION exhibited persistent facial pain-like behaviors and a significant increase in TRPC4 expression in TG neurons. Trpc4 shRNA or pharmacological inhibition with ML204 attenuated CION-induced pain behaviors, while activation of TRPC4 with Englerin A induced pain-like responses in naive mice. Calcium imaging revealed that both Englerin A and TRPC4 overexpression elevated intracellular Ca²2+ levels in TG neurons and HEK293 cells. This Ca²2+ influx triggered the activation of ERK and P38, leading to enhanced ATF2 activation. Downregulation of TRPC4 in the TG reduced ERK/P38 phosphorylation and ATF2 expression and activation.
Conclusion: This study provides the first evidence that TRPC4 plays a critical role in CION-induced trigeminal neuropathic pain by promoting the activation of the downstream transcription factor ATF2 via the Ca²2+-ERK/P38 pathway.
Keywords: ATF2; CION; Ca2+; ERK; P38; TRPC4; trigeminal neuropathic pain.
© 2025 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Zakrzewska J. M., “Differential Diagnosis of Facial Pain and Guidelines for Management,” British Journal of Anaesthesia 111, no. 1 (2013): 95–104. - PubMed
-
- Maarbjerg S., di Stefano G., Bendtsen L., and Cruccu G., “Trigeminal Neuralgia—Diagnosis and Treatment,” Cephalalgia 37, no. 7 (2017): 648–657. - PubMed
-
- Khairatkar‐Joshi N., Shah D. M., Mukhopadhyay I., Lingam V. S. P., and Thomas A., “TRPC Channel Modulators and Their Potential Therapeutic Applications,” Pharmaceutical Patent Analyst 4, no. 3 (2015): 207–218. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

