Human cytomegalovirus gH/gL/gO binding to PDGFRα provides a regulatory signal activating the fusion protein gB that can be blocked by neutralizing antibodies
- PMID: 40202318
- PMCID: PMC12090739
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00035-25
Human cytomegalovirus gH/gL/gO binding to PDGFRα provides a regulatory signal activating the fusion protein gB that can be blocked by neutralizing antibodies
Abstract
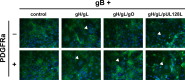
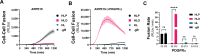
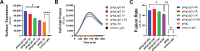
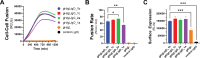
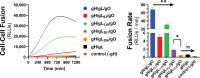
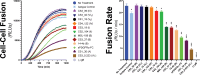
Herpesviruses require membrane fusion for entry and spread, a process facilitated by the fusion glycoprotein B (gB) and the regulatory factor gH/gL. The human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) gH/gL can be modified by the accessory protein gO, or the set of proteins UL128, UL130, and UL131. While the binding of the gH/gL/gO and gH/gL/UL128-131 complexes to cellular receptors, including PDGFRα and NRP2, has been well-characterized structurally, the specific role of receptor engagements by the gH/gL/gO and gH/gL/UL128-131 in regulation of fusion has remained unclear. We describe a cell-cell fusion assay that can quantitatively measure fusion on a timescale of minutes and demonstrate that binding of gH/gL/gO to PDGFRα dramatically enhances gB-mediated cell-cell fusion. In contrast, gH/gL/pUL128-131-regulated fusion is significantly slower, and gH/gL alone cannot promote gB fusion activity within this timescale. The genetic diversity of gO influenced the observed cell-cell fusion rates, correlating with previously reported effects on HCMV infectivity. Mutations in gL that had no effect on the formation of gH/gL/gO or binding to PDGFRa dramatically reduced the cell-cell fusion rate, suggesting that gL plays a critical role in linking the gH/gL/gO-PDGFRa receptor binding to activation of gB. Several neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies were found to potently block gH/gL/gO-PDGFRa-regulated cell-cell fusion, suggesting this mechanism as a therapeutic target.
Importance: Development of vaccines and therapeutics targeting the fusion apparatus of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) has been limited by the lack of an in vitro cell-cell fusion assay that faithfully models the receptor-dependent fusion characteristic of HCMV entry. The cell-cell fusion assay described here demonstrated that the binding of gH/gL/gO to its receptor, PDGFRα, serves to regulate the activity of the fusion protein gB, and this is specifically vulnerable to inhibition by neutralizing antibodies. Moreover, the measurement of fusion kinetics allows for mutational studies of the fusion mechanism, assessing the influence of genetic diversity among the viral glycoproteins and studying the mechanism of neutralizing antibodies.
Keywords: glycoproteins; human cytomegalovirus; membrane fusion; virus entry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Update of
-
Human cytomegalovirus gH/gL/gO binding to PDGFRα provides a regulatory signal activating the fusion protein gB that can be blocked by neutralizing antibodies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 8:2025.01.08.631902. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.08.631902. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Virol. 2025 May 20;99(5):e0003525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00035-25. PMID: 39829861 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Cell Fusion Induced by a Fusion-Active Form of Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein B (gB) Is Inhibited by Antibodies Directed at Antigenic Domain 5 in the Ectodomain of gB.J Virol. 2020 Aug 31;94(18):e01276-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01276-20. Print 2020 Aug 31. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32641474 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus gH/gL/gO binding to PDGFRα provides a regulatory signal activating the fusion protein gB that can be blocked by neutralizing antibodies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 8:2025.01.08.631902. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.08.631902. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Virol. 2025 May 20;99(5):e0003525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00035-25. PMID: 39829861 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus gH/gL/gO Promotes the Fusion Step of Entry into All Cell Types, whereas gH/gL/UL128-131 Broadens Virus Tropism through a Distinct Mechanism.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(17):8999-9009. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01325-15. Epub 2015 Jun 17. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26085146 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogen at the Gates: Human Cytomegalovirus Entry and Cell Tropism.Viruses. 2018 Dec 11;10(12):704. doi: 10.3390/v10120704. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30544948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From recognition to execution-the HCMV Pentamer from receptor binding to fusion triggering.Curr Opin Virol. 2018 Aug;31:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2018.05.004. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Curr Opin Virol. 2018. PMID: 29866439 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

