Liraglutide Treatment Reverses Unconventional Cellular Defects in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived β-Cells Harboring a Partially Functional WFS1 Variant
- PMID: 40202504
- PMCID: PMC12185971
- DOI: 10.2337/db24-0720
Liraglutide Treatment Reverses Unconventional Cellular Defects in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived β-Cells Harboring a Partially Functional WFS1 Variant
Erratum in
-
Erratum. Liraglutide Treatment Reverses Unconventional Cellular Defects in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived β-Cells Harboring a Partially Functional WFS1 Variant. Diabetes 2025;74:1273-1288.Diabetes. 2025 Aug 5:db25er10a. doi: 10.2337/db25-er10a. Online ahead of print. Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40763279
Abstract
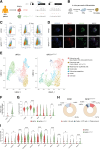
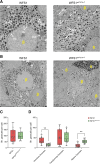
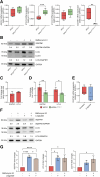
Wolfram syndrome 1 (WS1) is a rare genetic disorder caused by WFS1 variants that disrupt wolframin, an endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein essential for cellular stress responses, Ca2+ homeostasis, and autophagy. Here, we investigated how the c.316-1G>A and c.757A>T WFS1 mutations, which yield partially functional wolframin, affect the molecular functions of β-cells and explored the therapeutic potential of the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonist liraglutide. Pancreatic β-cells obtained from patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) carrying this WFS1 variant exhibited reduced insulin processing and impaired secretory granule maturation, as evidenced by proinsulin accumulation and decreased prohormone convertase PC1/3. Moreover, they exhibited dysregulated Ca2+ fluxes due to altered transcription of Ca2+-related genes, including CACNA1D, and significantly reduced SNAP25 levels, leading to uncoordinated oscillations and poor glucose responsiveness. Affected cells also showed increased autophagic flux and heightened susceptibility to inflammatory cytokine-induced apoptosis. Notably, liraglutide treatment rescued these defects by normalizing Ca2+ handling, enhancing insulin processing and secretion, and reducing apoptosis, likely through modulation of the unfolded protein response. These findings underscore the importance of defining mutation-specific dysfunctions in WS1 and support targeting the GLP-1/GLP-1R axis as a therapeutic strategy.
Article highlights: The molecular basis of WFS1-related mutations remains poorly investigated, and no definitive therapies exist for Wolfram syndrome 1. We dissected the molecular defects associated with c.316-1G>A and c.757A>T WFS1 mutations in patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cell islets and analyzed whether they are potential therapeutic targets of the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist liraglutide. We found impaired insulin granule maturation, altered Ca2+ fluxes, increased autophagic activity, and heightened susceptibility to inflammatory apoptosis in mutated cells. Liraglutide restored critical β-cell functions suggesting a route for personalized therapy based on WFS1 mutations.
© 2025 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
A WFS1 variant disrupting acceptor splice site uncovers the impact of alternative splicing on beta cell apoptosis in a patient with Wolfram syndrome.Diabetologia. 2025 Jan;68(1):128-151. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06307-0. Epub 2024 Nov 9. Diabetologia. 2025. PMID: 39520565 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1 receptor signaling increases PCSK1 and β cell features in human α cells.JCI Insight. 2021 Feb 8;6(3):e141851. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.141851. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 33554958 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of GLP-1 receptor signalling alleviates cellular stresses and improves beta cell function in a mouse model of Wolfram syndrome.Diabetologia. 2018 Oct;61(10):2189-2201. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4679-y. Epub 2018 Jul 28. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 30054673
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 analogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 10;5(5):CD012204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28489279 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of ER Stress in Diabetes: Exploring Pathological Mechanisms Using Wolfram Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 23;24(1):230. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010230. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rigoli L, Bramanti P, Di Bella C, De Luca F. Genetic and clinical aspects of Wolfram syndrome 1, a severe neurodegenerative disease. Pediatr Res 2018;83:921–929 - PubMed
-
- Takei D, Ishihara H, Yamaguchi S, et al. WFS1 protein modulates the free Ca(2+) concentration in the endoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett 2006;580:5635–5640 - PubMed
-
- Osman AA, Saito M, Makepeace C, Permutt MA, Schlesinger P, Mueckler M. Wolframin expression induces novel ion channel activity in endoplasmic reticulum membranes and increases intracellular calcium. J Biol Chem 2003;278:52755–52762 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

