Osteopontin, kidney injury molecule-1, and fetuin-A as prognostic markers of end-stage renal disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40202988
- PMCID: PMC11981136
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320804
Osteopontin, kidney injury molecule-1, and fetuin-A as prognostic markers of end-stage renal disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The global prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) as a major renal disease is increasing rapidly. The progression of CKD may lead to end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Current diagnostic and prognostic methods still have some limitations. This study aims to evaluate the potential and predictive ability of Osteopontin (OPN), Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), and Fetuin-A on the incidence of ESRD in CKD patients.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were carried out based on the PRISMA guideline on registered databases for studies published up to December 21, 2023. The concentrations of each marker were then reported in pooled standardized mean difference (SMD) and hazard ratio (HR). Subgroup analysis was performed based on age, location, and KIM-1 specimen.
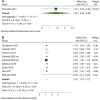
Results: We included 21 studies involving 15,983 patients. Meta-analysis revealed that increasing OPN (SMD = 5.52, 95% CI = 1.59-9.44, p = 0.01) and KIM-1 (SMD = 1.45, 95% CI = 0.50-2.39, p = 0.0027), as well as decreasing Fetuin-A level (SMD = -1.31, 95% CI = -2.37 - -0.26, p = 0.01) were significant in CKD patients with ESRD. Chronic kidney disease patients with increased KIM-1 levels showed 1.13 times increased risk of ESRD (HR = 1.13, 95% CI = 1.10-1.17, p <0.0001). Subgroup analysis showed that increased KIM-1 in urine or blood was strongly associated with ESRD, and decreased Fetuin-A levels in Asians had a significant association with the incidence of ESRD.
Conclusion: Osteopontin, KIM-1, and Fetuin-A significantly reflect ESRD in CKD patients, making them potential prognostic indicators.
Copyright: © 2025 Welliam et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomarkers of vascular calcification and mortality in patients with ESRD.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Apr;9(4):745-55. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05450513. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24458076 Free PMC article.
-
The Associations of Blood Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin with Progression from CKD to ESRD.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Dec 7;11(12):2141-2149. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02670316. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27852662 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular calcification is not related to serum fetuin-A and osteopontin levels in hemodialysis patients.Int Urol Nephrol. 2018 Jan;50(1):137-142. doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1740-6. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29134617
-
Associations of Proton-Pump Inhibitors and H2 Receptor Antagonists with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 Oct;62(10):2821-2827. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4725-5. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28836158 Review.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes of lower extremity peripheral arterial interventions in patients with and without chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal disease.J Vasc Surg. 2021 Jan;73(1):331-340.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2020.08.032. Epub 2020 Sep 1. J Vasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 32889074
References
-
- Cheung AK, Chang TI, Cushman WC, Furth SL, Hou FF, Ix JH, et al.. KDIGO 2021 clinical practice guideline for the management of blood pressure in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2021;99(3):S1–87. - PubMed
-
- Kidey Disease. Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Nomenclature for Kidney Function and Disease. A KDIGO Consensus Conference on Nomenclature. 2019
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous