Condensin IDC, DPY-21, and CEC-4 maintain X chromosome repression in C. elegans
- PMID: 40203054
- PMCID: PMC12013946
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011247
Condensin IDC, DPY-21, and CEC-4 maintain X chromosome repression in C. elegans
Abstract
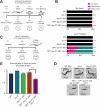
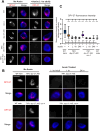
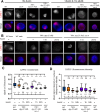
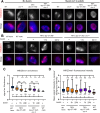
Dosage compensation in Caenorhabditis elegans equalizes X-linked gene expression between XX hermaphrodites and XO males. The process depends on a condensin-containing dosage compensation complex (DCC), which binds the X chromosomes in hermaphrodites to repress gene expression by a factor of 2. Condensin IDC and an additional five DCC components must be present on the X during early embryogenesis in hermaphrodites to establish dosage compensation. However, whether the DCC's continued presence is required to maintain the repressed state once established is unknown. Beyond the role of condensin IDC in X chromosome compaction, additional mechanisms contribute to X-linked gene repression. DPY-21, a non-condensin IDC DCC component, is an H4K20me2/3 demethylase whose activity enriches the repressive histone mark, H4 lysine 20 monomethylation, on the X chromosomes. In addition, CEC-4, a protein that tethers H3K9me3-rich chromosomal regions to the nuclear lamina, also contributes to X-linked gene repression. To investigate the necessity of condensin IDC during the larval and adult stages of hermaphrodites, we used the auxin-inducible degradation system to deplete the condensin IDC subunit DPY-27. While DPY-27 depletion in the embryonic stages resulted in lethality, DPY-27 depleted larvae and adults survive. In these DPY-27 depleted strains, condensin IDC was no longer associated with the X chromosome, the X became decondensed, and the H4K20me1 mark was gradually lost, leading to X-linked gene derepression (about 1.4-fold). These results suggest that the stable maintenance of dosage compensation requires the continued presence of condensin IDC. A loss-of-function mutation in cec-4, in addition to the depletion of DPY-27 or the genetic mutation of dpy-21, led to even more significant increases in X-linked gene expression (about 1.7-fold), suggesting that CEC-4 helps stabilize repression mediated by condensin IDC and H4K20me1.
Copyright: © 2025 Trombley et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Developmental Dynamics of X-Chromosome Dosage Compensation by the DCC and H4K20me1 in C. elegans.PLoS Genet. 2015 Dec 7;11(12):e1005698. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005698. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26641248 Free PMC article.
-
The histone H4 lysine 20 demethylase DPY-21 regulates the dynamics of condensin DC binding.J Cell Sci. 2022 Jan 15;135(2):jcs258818. doi: 10.1242/jcs.258818. Epub 2022 Jan 26. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 34918745 Free PMC article.
-
H4K20me1 contributes to downregulation of X-linked genes for C. elegans dosage compensation.PLoS Genet. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002933. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002933. Epub 2012 Sep 13. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23028348 Free PMC article.
-
Condensin function in dosage compensation.Epigenetics. 2009 May 16;4(4):212-5. doi: 10.4161/epi.8957. Epub 2009 May 7. Epigenetics. 2009. PMID: 19483464 Review.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans Dosage Compensation: Insights into Condensin-Mediated Gene Regulation.Trends Genet. 2018 Jan;34(1):41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2017.09.010. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Trends Genet. 2018. PMID: 29037439 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

