Asparagine transporter supports macrophage inflammation via histone phosphorylation
- PMID: 40203093
- PMCID: PMC11980831
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ads3506
Asparagine transporter supports macrophage inflammation via histone phosphorylation
Abstract
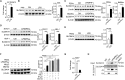
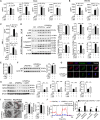
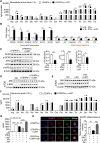
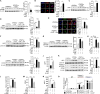
Solute carrier (SLC) family is essential for immune responses; nevertheless, whether and how SLCs regulate macrophage inflammation remains unclear. Here, we demonstrate that K636 acetylation mediates high abundance of SLC6A14 in inflammatory macrophages. Notably, the pharmacological inhibition or genetic modulation of SLC6A14 reduces macrophage interleukin-1β (IL-1β) secretion dependently of lower asparagine uptake and subsequently enhanced nuclear LKB1. Mechanistically, nuclear LKB1 lessens MAPK pathway-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation by increased histone 3 S10/28 phosphorylation-dependent cyclin O transcription. Moreover, myeloid Slc6a14 deficiency alleviates pulmonary inflammation via suppressing inflammatory macrophage responses. Overall, these results uncover a network by which SLC6A14-mediated asparagine uptake orchestrates macrophage inflammation through histone phosphorylation, providing a crucial target for modulation of inflammatory diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang J., Muri J., Fitzgerald G., Gorski T., Gianni-Barrera R., Masschelein E., D’Hulst G., Gilardoni P., Turiel G., Fan Z., Wang T., Planque M., Carmeliet P., Pellerin L., Wolfrum C., Fendt S. M., Banfi A., Stockmann C., Soro-Arnaiz I., Kopf M., De Bock K., Endothelial lactate controls muscle regeneration from ischemia by inducing M2-like macrophage polarization. Cell Metab. 31, 1136–1153.e7 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

