Intratumoral mycobiome heterogeneity influences the tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy outcomes in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40203108
- PMCID: PMC11980860
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adu1727
Intratumoral mycobiome heterogeneity influences the tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy outcomes in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
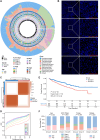
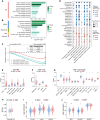
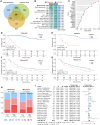
The intratumoral mycobiome plays a crucial role in the tumor microenvironment, but its impact on renal cell carcinoma (RCC) remains unclear. We collected and quantitatively profiled the intratumoral mycobiome data from 1044 patients with RCC across four international cohorts, of which 466 patients received immunotherapy. Patients were stratified into mycobiota ecology-depauperate and mycobiota ecology-flourishing (MEF) groups based on fungal abundance. The MEF group had worse prognosis, higher fungal diversity, down-regulated lipid catabolism, and exhausted CD8+ T cells. We developed the intratumoral mycobiota signature and intratumoral mycobiota-related genes expression signature, which robustly predicted prognosis and immunotherapy outcomes in RCC and other cancers. Aspergillus tanneri was identified as a potential key fungal species influencing RCC prognosis. Our findings suggest that the intratumoral mycobiome suppresses lipid catabolism and induces T cell exhaustion in RCC.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel R. L., Miller K. D., Wagle N. S., Jemal A., Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 73, 17–48 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Bui T. O., Dao V. T., Nguyen V. T., Feugeas J.-P., Pamoukdjian F., Bousquet G., Genomics of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 81, 349–361 (2022). - PubMed
-
- EAU Guidelines. Edn. presented at the EAU Annual Congress Paris 2024. ISBN 978-94-92671-23-3.
-
- Nejman D., Livyatan I., Fuks G., Gavert N., Zwang Y., Geller L. T., Rotter-Maskowitz A., Weiser R., Mallel G., Gigi E., Meltser A., Douglas G. M., Kamer I., Gopalakrishnan V., Dadosh T., Levin-Zaidman S., Avnet S., Atlan T., Cooper Z. A., Arora R., Cogdill A. P., Khan M. A. W., Ologun G., Bussi Y., Weinberger A., Lotan-Pompan M., Golani O., Perry G., Rokah M., Bahar-Shany K., Rozeman E. A., Blank C. U., Ronai A., Shaoul R., Amit A., Dorfman T., Kremer R., Cohen Z. R., Harnof S., Siegal T., Yehuda-Shnaidman E., Gal-Yam E. N., Shapira H., Baldini N., Langille M. G. I., Ben-Nun A., Kaufman B., Nissan A., Golan T., Dadiani M., Levanon K., Bar J., Yust-Katz S., Barshack I., Peeper D. S., Raz D. J., Segal E., Wargo J. A., Sandbank J., Shental N., Straussman R., The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type-specific intracellular bacteria. Science 368, 973–980 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

