Unraveling the effects of uric acid on endothelial cells: A global proteomic study
- PMID: 40203480
- PMCID: PMC12005352
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103625
Unraveling the effects of uric acid on endothelial cells: A global proteomic study
Abstract
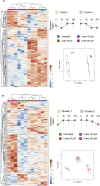
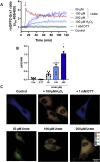
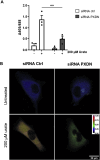
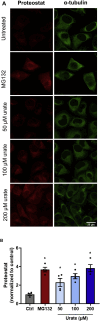
This work aims to understand how normouricemic levels of uric acid can induce endothelial dysfunction seeking global proteomic alterations in Human Umbilical Vein cells (HUVEC). It reveals significant alterations in redox-sensitive and antioxidant proteins, chaperones, and proteins associated with cell migration and adhesion in response to uric acid exposure. Monitoring cellular oxidation with the roGFP2-Grx1 probe proved increased oxidation levels induced by uric acid, which can be attenuated by peroxidasin (PXDN) inhibition, suggesting a regulatory role for PXDN in mitigating oxidative stress induced by uric acid. As a consequence of uric acid oxidation and the formation of reactive intermediate, we identified adducts in proteins (+140 kDa) in a novel post-translation modification named uratylation. Increased misfolded protein levels and p62 aggregation were also found, indicating disturbances in cellular proteostasis. Furthermore, uric acid promoted monocyte adhesion and upregulated ICAM and VCAM protein levels, implicating a pro-inflammatory response in endothelial cells. These findings provide critical insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying vascular damage associated with uric acid.
Keywords: Endothelial cell damage; HUVEC; Inflammation; PXDN; Proteomics; Uric acid.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Lipid Variability Induces Endothelial Dysfunction by Increasing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2024 Jun;39(3):511-520. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.1915. Epub 2024 May 16. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 38752267 Free PMC article.
-
Uric acid induced inflammatory responses in endothelial cells via up-regulating(pro)renin receptor.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:1163-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.129. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551366
-
Protective Effect of Uric Acid on ox-LDL-Induced HUVECs Injury via Keap1-Nrf2-ARE Pathway.J Immunol Res. 2021 Nov 1;2021:5151168. doi: 10.1155/2021/5151168. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34761008 Free PMC article.
-
Uric acid promotes chemokine and adhesion molecule production in vascular endothelium via nuclear factor-kappa B signaling.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Feb;25(2):187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25315669
-
At the interface of antioxidant signalling and cellular function: Key polyphenol effects.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016 Aug;60(8):1770-88. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500940. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016. PMID: 26887821 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Is uric acid a true antioxidant? Identification of uric acid oxidation products and their biological effects.Redox Rep. 2025 Dec;30(1):2498105. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2025.2498105. Epub 2025 May 25. Redox Rep. 2025. PMID: 40415203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Becker B.F. Towards the physiological function of uric acid. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1993;14:615–631. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

