Causal associations between environmental factors and risk of IgA nephropathy and membranous nephropathy: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization and mediation analysis
- PMID: 40204511
- PMCID: PMC11983537
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2486620
Causal associations between environmental factors and risk of IgA nephropathy and membranous nephropathy: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization and mediation analysis
Abstract
Aims: IgA nephropathy (IgAN) and membranous nephropathy (MN) have intricate etiologies that are poorly understood. This study aimed to investigate the impact of genetically predicted environmental factors on IgAN and MN.
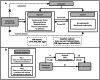
Methods: We used bidirectional two-step Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis utilizing large-scale genome-wide association study (GWAS) data to investigate the relationships between 68 environmental exposures and IgAN and MN. The main method is inverse variance weighted (IVW). Sensitivity analyses were conducted to validate the causal estimates. Furthermore, the two-step MR was used to explore possible mediating effects.
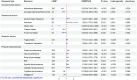
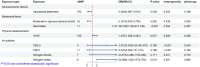
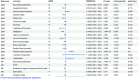
Results: A total of 20 significant causal associations were identified. Genetically predicted educational attainment (EA), average household income, gluten-free diet, cheese intake, fresh fruit intake, cognitive performance, and intelligence were associated with a reduced risk of IgAN (p < 0.05); whereas frequency of alcohol consumption, insomnia, triglycerides, transferrin saturation, percentage body fat, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, and blood pressure were associated with the risk of IgAN (p < 0.05). Genetically predicted EA and moderate to vigorous physical activity were associated with a reduced risk of MN (p < 0.05); on the other hand, beef intake, waist-to-hip ratio, and nitrogen oxides were associated with the risk of MN (p < 0.05). In addition, we observed that insomnia, BMI, and waist circumference partially mediated the causal link between EA and IgAN, with mediation proportions of 12.52%, 11.06%, and 9.93%, respectively.
Conclusions: This study provides novel evidence of causal relationships between 20 genetically predicted environmental factors and the risk of IgAN and MN. These findings may inform targeted prevention strategies and contribute to improved disease risk assessment.
Keywords: Environmental exposures; IgA nephropathy; mediation analysis; membranous nephropathy; mendelian randomization; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis of the causal associations between serum vitamin D levels and multiple kidney diseases.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 4;15(1):23908. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10305-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40615622 Free PMC article.
-
Causal association between peripheral immune cells and IgA nephropathy: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 16;15:1371662. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1371662. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39221249 Free PMC article.
-
Causal effects between gut microbiota and IgA nephropathy: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 May 2;13:1171517. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1171517. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37201114 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between gluten-free diet and IgA nephropathy: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 13;104(24):e41964. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041964. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40527780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Present and Future of IgA Nephropathy and Membranous Nephropathy Immune Monitoring: Insights from Molecular Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 23;24(17):13134. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713134. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37685941 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
