GRAMD1B is a regulator of lipid homeostasis, autophagic flux and phosphorylated tau
- PMID: 40204713
- PMCID: PMC11982250
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58585-w
GRAMD1B is a regulator of lipid homeostasis, autophagic flux and phosphorylated tau
Abstract
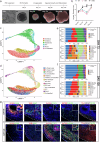
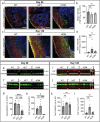
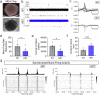
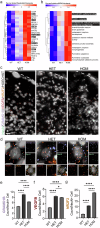
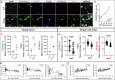
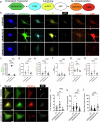
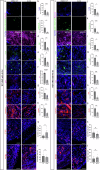
Lipid dyshomeostasis and tau pathology are present in frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the relationship between lipid dyshomeostasis and tau pathology remains unclear. We report that GRAM Domain Containing 1B (GRAMD1B), a nonvesicular cholesterol transporter, is increased in excitatory neurons of human neural organoids (HNOs) with the MAPT R406W mutation. Human FTLD, AD cases, and PS19 tau mice also have increased GRAMD1B expression. We show that overexpression of GRAMD1B increases levels of free cholesterol, lipid droplets, and impairs autophagy flux. Modulating GRAMD1B in iPSC-derived neurons also alters key autophagy-related components such as PI3K, phospho-AKT, and p62, as well as phosphorylated tau, and CDK5R1. Blocking GRAMD1B function decreases free cholesterol and lipid droplets. Knocking down GRAMD1B additionally reduces phosphorylated tau, and CDK5R1 expression. Our findings elucidate the role of GRAMD1B in the nervous system and highlight its relevance to FTLD and AD.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mirra, S. S. et al. Tau pathology in a family with dementia and a P301L mutation in tau. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol.58, 335–345 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Spillantini, M. G., Van Swieten, J. C. & Goedert, M. Tau gene mutations in frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17). Neurogenetics2, 193–205 (2000). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS110890/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG075092/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG044271/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- A2021027S/BrightFocus Foundation (BrightFocus)
- U24 NS072026/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG066444/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- R56 NS110890/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG072980/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AG075092-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS110890/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- P30 AG072980/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013319/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS110890/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066462/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

