3-Dimensional printing and bioprinting in neurological sciences: applications in surgery, imaging, tissue engineering, and pharmacology and therapeutics
- PMID: 40205004
- PMCID: PMC11982170
- DOI: 10.1007/s10856-025-06877-4
3-Dimensional printing and bioprinting in neurological sciences: applications in surgery, imaging, tissue engineering, and pharmacology and therapeutics
Abstract
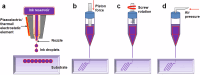
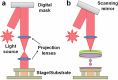
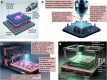
The rapid evolution of three-dimensional printing (3DP) has significantly impacted the medical field. In neurology for instance, 3DP has been pivotal in personalized surgical planning and education. Additionally, it has facilitated the creation of implants, microfluidic devices, and optogenetic probes, offering substantial implications for medical and research applications. Additionally, 3D printed nasal casts are showing great promise for targeted brain drug delivery. 3DP has also aided in creating 3D "phantoms" aligning with advancements in neuroimaging, and in the design of intricate objects for investigating the neurobiology of sensory perception. Furthermore, the emergence of 3D bioprinting (3DBP), a fusion of 3D printing and cell biology, has created new avenues in neural tissue engineering. Effective and ethical creation of tissue-like biomimetic constructs has enabled mechanistic, regenerative, and therapeutic evaluations. While individual reviews have explored the applications of 3DP or 3DBP, a comprehensive review encompassing the success stories across multiple facets of both technologies in neurosurgery, neuroimaging, and neuro-regeneration has been lacking. This review aims to consolidate recent achievements of both 3DP and 3DBP across various neurological science domains to encourage interdisciplinary research among neurologists, neurobiologists, and engineers, in order to promote further exploration of 3DP and 3DBP methodologies to novel areas of neurological science research and practice.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Innovative 3D bioprinting approaches for advancing brain science and medicine: a literature review.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024 Sep 25;10(6). doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ad795c. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024. PMID: 39260389 Review.
-
Three-dimensional printing: The potential technology widely used in medical fields.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020 Nov 1;108(11):2217-2229. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36979. Epub 2020 Jun 20. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020. PMID: 32363725 Review.
-
Advances in 4D Bioprinting: The Next Frontier in Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering Applications.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Feb;14(4):e2403065. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202403065. Epub 2024 Dec 29. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 39918399 Review.
-
Photocrosslinkable Biomaterials for 3D Bioprinting: Mechanisms, Recent Advances, and Future Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 22;25(23):12567. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312567. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4D Printing for Biomedical Applications.Adv Mater. 2024 Aug;36(31):e2402301. doi: 10.1002/adma.202402301. Epub 2024 May 28. Adv Mater. 2024. PMID: 38580291 Review.
References
-
- Sharma A, Anand S, Bharti PS. 13 3D printing insight: techniques, application, and transformation. 3D Print Technol. De Gruyter; 2024. p. 259–88. Available from: https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/9783111215112-013/html - DOI
-
- Kholgh Eshkalak S, Rezvani Ghomi E, Dai Y, Choudhury D, Ramakrishna S. The role of three-dimensional printing in healthcare and medicine. Mater Des. 2020;194:108940. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0264127520304743.
-
- Gander C, Shi K, Nokhodchi A, Lam M. A review of the benefits 3D printing brings to patients with neurological diseases. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15:892. https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/15/3/892. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kutlehria S, D’Souza A, Bleier BS, Amiji MM. Role of 3D printing in the development of biodegradable implants for central nervous system drug delivery. Mol Pharm. 2022;19:4411–27. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00344. - DOI - PubMed
-
- He J, Qiao L, Li J, Lu J, Fu Z, Chen J, et al. Advanced strategies for 3D-printed neural scaffolds: materials, structure, and nerve remodeling. Bio-Design Manuf. 2024;7:747–70. https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s42242-024-00291-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

