Comprehensive interrogation of synthetic lethality in the DNA damage response
- PMID: 40205037
- PMCID: PMC12018271
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08815-4
Comprehensive interrogation of synthetic lethality in the DNA damage response
Abstract
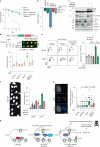
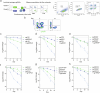
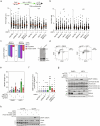
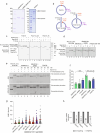
The DNA damage response (DDR) is a multifaceted network of pathways that preserves genome stability1,2. Unravelling the complementary interplay between these pathways remains a challenge3,4. Here we used CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) screening to comprehensively map the genetic interactions required for survival during normal human cell homeostasis across all core DDR genes. We captured known interactions and discovered myriad new connections that are available online. We defined the molecular mechanism of two of the strongest interactions. First, we found that WDR48 works with USP1 to restrain PCNA degradation in FEN1/LIG1-deficient cells. Second, we found that SMARCAL1 and FANCM directly unwind TA-rich DNA cruciforms, preventing catastrophic chromosome breakage by the ERCC1-ERCC4 complex. Our data yield fundamental insights into genome maintenance, provide a springboard for mechanistic investigations into new connections between DDR factors and pinpoint synthetic vulnerabilities that could be exploited in cancer therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.E.C. is a cofounder and scientific advisory board (SAB) member of Serac Biosciences; an SAB member of Mission Therapeutics, Relation Therapeutics and Hornet Biologicals; and a consultant for Cimeio Therapeutics. S.P.J. is shareholder and part-time chief research officer of Insmed Innovation UK, board member and chair of scientific advisory board for Mission Therapeutics and a founding partner of Ahren Innovation Capital. All other authors have no competing interests.
Figures












References
-
- Tong, A. H. Y. et al. Global mapping of the yeast genetic interaction network. Science303, 808–813 (2004). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

