Immune checkpoint TIM-3 regulates microglia and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 40205047
- PMCID: PMC12079183
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08852-z
Immune checkpoint TIM-3 regulates microglia and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
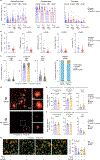
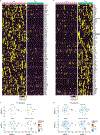
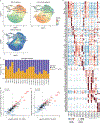
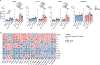
Microglia are the resident immune cells in the brain and have pivotal roles in neurodevelopment and neuroinflammation1,2. This study investigates the function of the immune-checkpoint molecule TIM-3 (encoded by HAVCR2) in microglia. TIM-3 was recently identified as a genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease3, and it can induce T cell exhaustion4. However, its specific function in brain microglia remains unclear. We demonstrate in mouse models that TGFβ signalling induces TIM-3 expression in microglia. In turn, TIM-3 interacts with SMAD2 and TGFBR2 through its carboxy-terminal tail, which enhances TGFβ signalling by promoting TGFBR-mediated SMAD2 phosphorylation, and this process maintains microglial homeostasis. Genetic deletion of Havcr2 in microglia leads to increased phagocytic activity and a gene-expression profile consistent with the neurodegenerative microglial phenotype (MGnD), also referred to as disease-associated microglia (DAM). Furthermore, microglia-targeted deletion of Havcr2 ameliorates cognitive impairment and reduces amyloid-β pathology in 5×FAD mice (a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease). Single-nucleus RNA sequencing revealed a subpopulation of MGnD microglia in Havcr2-deficient 5×FAD mice characterized by increased pro-phagocytic and anti-inflammatory gene expression alongside reduced pro-inflammatory gene expression. These transcriptomic changes were corroborated by single-cell RNA sequencing data across most microglial clusters in Havcr2-deficient 5×FAD mice. Our findings reveal that TIM-3 mediates microglia homeostasis through TGFβ signalling and highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting microglial TIM-3 in Alzheimer's disease.
© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: G.J.F. has equity in Nextpoint, iTeos, IgM, Invaria, GV20, Bioentre and Geode. G.J.F. has served on advisory boards for iTeos, NextPoint, IgM, GV20, IOME, Bioentre, Santa Ana Bio, Simcere of America and Geode. G.J.F.’s interests were reviewed and managed by the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in accordance with their conflict-of-interest policies. D.J.S. is a director of Prothena Biosciences and an ad hoc consultant to Roche and Eisai. M.B.-J. is a co-founder and consultant for Savanna Biotherapeutics (formally NovoGlia). A.R. is a cofounder and equity holder of Celsius Therapeutics, an equity holder in Immunitas and was a scientific advisory board member of ThermoFisher Scientific, Syros Pharmaceuticals, Neogene Therapeutics and Asimov until 31 July 2020. From 1 August 2020, A.R. is an employee of Genentech and has equity in Roche. M.L.S. is an equity holder, scientific cofounder and advisory board member of Immunity Therapeutics. O.B. is a cofounder of and has an ownership interest in Glial Therapeutics and Gliax. O.B. has a financial interest in Glial Therapeutics, a company developing a new therapy to target ITGB8–TGFβ signalling as a treatment for AD. O.B.’s interests were reviewed and are managed by Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Mass General Brigham in accordance with their conflict-of-interest policies and include collaboration with GSK and Regulus Therapeutics, receiving research funding from Sanofi and GSK, and honoraria for lectures and consultancy from UCB, Camp4 and Ono Pharma USA. V.K.K. has an ownership interest in Tizona Therapeutics, Trishula, Celsius Therapeutics, Bicara Therapeutics, Larkspur Therapeutics and Werewolf Therapeutics. V.K.K. has financial interests in Biocon Biologic, Compass, Elpiscience Biopharmaceutical, Equilium, PerkinElmer and Syngene. V.K.K. is a member of SABs for Cell Signaling Technology, Elpiscience Biopharmaceutical, Larkspur, Tizona Therapeutics, Tr1X and Werewolf. V.K.K.’s interests were reviewed and managed by Mass General Brigham in accordance with their conflict-of-interest policies.
Figures














References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RF1 AG082704/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG075509/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY027921/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066519/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054672/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI073748/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG051812/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS088137/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG076982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG080992/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG069701/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI144166/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

