Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 blockage attenuates pyroptosis in hippocampus of mice following pilocarpine‑induced status epilepticus
- PMID: 40205503
- PMCID: PMC11983898
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-025-01990-5
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 blockage attenuates pyroptosis in hippocampus of mice following pilocarpine‑induced status epilepticus
Abstract
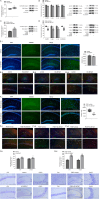
Pyroptosis contributes to the neuronal damage that occurs during epilepsy. Calcium-activated neutral protease (calpain) dissociates cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase-1 (caspase-1, cas-1) from the cytoskeleton, and the activated cas-1 is responsible for the production of N-terminus of gasdermin D (N-GSDMD), the final executor of pyroptosis. Blocking transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) can reduce neuronal injury in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) model mice. This study investigated the role of TRPV4 in pyroptosis during TLE. In the hippocampus of pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus (PISE) mice, the ratio of inactive calpain 1 protein level to its total protein level (inactive/total calpain 1) significantly decreased, while the ratio of inactive calpain 2 protein level to its total protein level remained unchanged. The protein levels of NLRP3, cleaved cas-1 (c-cas-1), interleukin (IL)-1β, and N-GSDMD increased, with more GSDMD-immunofluorescence-positive (GSDMD+) cells and fewer surviving pyramidal neurons observed in the hippocampus of PISE mice. Calpain inhibition with MDL-28170 reversed these changes, except for the elevated NLRP3 levels. Inhibitors targeting NLRP3 (MCC950) and cas-1 (Ac-YVAD-cmk) blocked the increase in c-cas-1, IL-1β, and N-GSDMD levels in the hippocampus of PISE mice. TRPV4 inhibition via HC-067047 increased the inactive/total calpain 1 ratio, decreased NLRP3, c-cas-1, IL-1β, and N-GSDMD protein levels, reduced GSDMD+ cells number, and improved pyramidal neuron survival in the hippocampus of PISE mice. Conversely, TRPV4 activation with GSK1016790A decreased the inactive/total calpain 1 ratio, elevated NLRP3, c-cas-1, IL-1β, and N-GSDMD levels, and increased GSDMD+ cells number in the hippocampus. In the hippocampus of GSK1016790A-injected mice, the inactive/total calpain 1 ratio was increased by MDL-28170, and c-cas-1, IL-1β, and N-GSDMD protein levels were markedly attenuated by MDL-28170, MCC950, and Ac-YVAD-cmk, respectively. In conclusion, TRPV4 inhibition mitigates pyroptosis in PISE mice by downregulating the calpain 1-NLRP3/cas-1-GSDMD pathway, ultimately reducing neuronal damage.
Keywords: Calpain; Caspase-1; Gasdermin D; Pyroptosis; Temporal lobe epilepsy; Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanjing Medical University (No. IACUC2009007), and all animal experiments were performed in accordance with the Guidelines for Laboratory Animal Research set by Nanjing Medical University. All efforts were made to minimize animal suffering and to reduce the number of animals used. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
TRPV4-induced inflammatory response is involved in neuronal death in pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy in mice.Cell Death Dis. 2019 May 16;10(6):386. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1612-3. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31097691 Free PMC article.
-
Direct inhibition of the TXNIP-NLRP3-GSDMD pathway reduces pyroptosis in colonocytes and alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by the small compound PEITC.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Sep;46(9):2436-2449. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01549-z. Epub 2025 Apr 7. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40195510
-
Effects of Baicalein Pretreatment on the NLRP3/GSDMD Pyroptosis Pathway and Neuronal Injury in Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus in the Mice.eNeuro. 2025 Jan 8;12(1):ENEURO.0319-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0319-24.2024. Print 2025 Jan. eNeuro. 2025. PMID: 39662962 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis: implications in inflammation and multisystem disorders.PeerJ. 2025 Aug 15;13:e19887. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19887. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40832584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights on the Potential Role of Pyroptosis in Parkinson's Neuropathology and Therapeutic Targeting of NLRP3 Inflammasome with Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-Based miRNA Therapeutics.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul;62(7):9365-9384. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04818-4. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40100493 Review.
References
-
- Henshall DC, Chen J, Simon RP (2000) Involvement of caspase-3-like protease in the mechanism of cell death following focally evoked limbic seizures. J Neurochem 74(3):1215–1223. 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.741215.x - PubMed
-
- Mohseni-Moghaddam P, Roghani M, Khaleghzadeh-Ahangar H, Sadr SS, Sala C (2021) A literature overview on epilepsy and inflammasome activation. Brain Res Bull 172:229–235. 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.05.001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

