Association between neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and hearing loss: a cross-sectional study from NHANES
- PMID: 40205514
- PMCID: PMC11983788
- DOI: 10.1186/s41043-025-00851-0
Association between neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and hearing loss: a cross-sectional study from NHANES
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the relationship between the neutrophil-to-HDL cholesterol ratio (NHR) and the risk of hearing loss, as well as to evaluate the potential of the NHR as a biomarker for hearing loss.
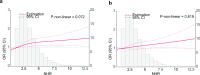
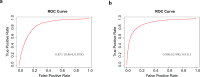
Methods: The U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data covering 2005-2012 and 2015-2020 were analyzed. A weighted multivariate logistic regression model assessed the correlation between NHR and speech-frequency hearing loss (SFHL) and high-frequency hearing loss (HFHL). Restricted cubic spline (RCS) regression analysis was utilized to investigate the nonlinear correlation. Additionally, subgroup analysis was performed to identify differences among subgroups. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was conducted to evaluate the efficacy of NHR in predicting hearing loss.
Results: A total of 10,436 participants were involved. After comprehensive adjustments for confounding factors, NHR was linearly correlated with SFHL and HFHL. Subgroup analysis revealed that race and the poverty index ratio (PIR) significantly modified the association between NHR and hearing loss. ROC analysis demonstrated the predictive capability of NHR for hearing loss.
Conclusion: NHR is positively correlated with the risk of hearing loss. This study suggests that NHR may serve as a potential biomarker for predicting and assessing hearing loss, demonstrating significant clinical application value. However, this cross-sectional study limits the ability to establish causality. Future longitudinal studies are needed to confirm these findings and explore potential mechanisms.
Keywords: High-frequency hearing loss; NHANES; Speech-frequency hearing loss; neutrophil-to-HDL cholesterol ratio.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Data for this study was collected from the NHANES database. Approval was obtained from the Research Ethics Review Board of the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). All participants provided written informed consent, ensuring compliance with relevant local laws and regulations to uphold the legality of the research. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association between neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and gallstones: a cross-sectional study.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 14;25(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21392-5. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39810139 Free PMC article.
-
Association between neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and liver fibrosis in the US population: a nationally representative cross-sectional study using NHANES data from 2017 to 2020.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 5;24(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03394-6. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39237899 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with kidney stone risk: a cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 3;16:1523890. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1523890. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39963279 Free PMC article.
-
Association between neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHR) and depression symptoms among the United States adults: a cross-sectional study.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jul 13;23(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02204-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39003458 Free PMC article.
-
Association between high-density lipoprotein-related inflammation index and periodontitis: insights from NHANES 2009-2014.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Sep 28;23(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02312-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39342327 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil-to-High density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio predicts early hematoma expansion in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Jun 30;48(1):533. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03682-z. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 40583091
References
-
- World report on. Hearing: executive summary. Geneva: World Health Organization 2021. Licence. CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
-
- Disease GBD, Injury I, Prevalence C. Global, regional, and National incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet Oct. 2016;8(10053):1545–602. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Global costs of unaddressed hearing loss and cost-effectiveness of interventions: a WHO report. 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
-
- Michels TC, Duffy MT, Rogers DJ. Hearing loss in adults: differential diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician Jul. 2019;15(2):98–108. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

